Lignans from Tujia Ethnomedicine Heilaohu: Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxicity and Antioxidant Activities
- PMID: 30150546
- PMCID: PMC6225210
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23092147
Lignans from Tujia Ethnomedicine Heilaohu: Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxicity and Antioxidant Activities
Abstract
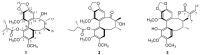
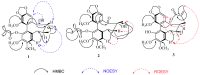
Heilaohu, the roots of Kadsura coccinea, has a long history of use in Tujia ethnomedicine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and gastroenteric disorders, and a lot of work has been done in order to know the material basis of its pharmacological activities. The chemical investigation led to the isolation and characterization of three new (1⁻3) and twenty known (4⁻23) lignans. Three new heilaohulignans A-C (1⁻3) and seventeen known (4⁻20) lignans possessed dibenzocyclooctadiene skeletons. Similarly, one was a diarylbutane (21) and two were spirobenzofuranoid dibenzocyclooctadiene (22⁻23) lignans. Among the known compounds, 4⁻5, 7, 13⁻15 and 17⁻22 were isolated from this species for the first time. The structures were established, using IR, UV, MS and NMR data. The absolute configurations of the new compounds were determined by circular dichroism (CD) spectra. The isolated lignans were further evaluated for their cytotoxicity and antioxidant activities. Compound 3 demonstrated strong cytotoxic activity with an IC50 value of 9.92 µM, compounds 9 and 13 revealed weak cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 21.72 µM and 18.72 µM, respectively in the HepG-2 human liver cancer cell line. Compound 3 also showed weak cytotoxicity against the BGC-823 human gastric cancer cell line and the HCT-116 human colon cancer cell line with IC50 values of 16.75 µM and 16.59 µM, respectively. A chemiluminescence assay for antioxidant status of isolated compounds implied compounds 11 and 20, which showed weak activity with IC50 values of 25.56 µM and 21.20 µM, respectively.
Keywords: antioxidant; chemical characterization; cytotoxicity; heilaohu; lignans; tujia ethnomedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jian S., Yao J., Huang S., Xing L., Wang J., García-García E. Antioxidant activity of polyphenol and anthocyanin extracts from fruits of Kadsura coccinea (Lem.) A.C. Smith. Food Chem. 2009;117:276–281.
-
- Chen D.F., Zhang S.X., Kozuka M., Sun Q.Z., Feng J., Wang Q., Mukainaka T., Nobukuni Y., Tokuda H., Nishino H., et al. Interiotherins C and D, two new lignans from Kadsura interior and antitumor-promoting effects of related neolignans on epstein-barr virus activation. J. Nat. Prod. 2002;65:1242–1245. doi: 10.1021/np0105127. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical