Rapid Regeneration and Reuse of Silica Columns from PCR Purification and Gel Extraction Kits
- PMID: 30150610
- PMCID: PMC6110862
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30316-w
Rapid Regeneration and Reuse of Silica Columns from PCR Purification and Gel Extraction Kits
Abstract
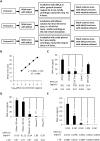
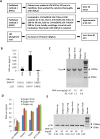
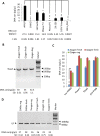
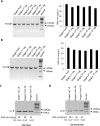
Silica columns from PCR purification and gel extraction kits are widely used in laboratories worldwide to assist in gene cloning. However, the use of these columns can generate plastic waste that has an environmental impact due to their one-off design and massive consumption. Thus, it is important to develop a novel method that can reduce the utilization of silica columns but not affect research efficiency. In this study, various chemical and nonchemical reagents were used to eliminate residual DNA within used columns from PCR purification and gel extraction kits. We show that phosphoric acid is the most effective reagent among those tested to remove DNA contamination from used columns. Columns regenerated using 1 M phosphoric acid have a DNA purification capability that is comparable to that of fresh columns. We demonstrate that silica columns can be regenerated and reused a minimum of five times. The lab-made buffers are compatible with the regenerated columns for DNA purification, and DNA that is prepared with the regenerated columns can be used for gene cloning without affecting the gene cloning efficiency. Thus, the use of this novel method greatly reduces the production of laboratory waste and benefits numerous laboratories worldwide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regenerated silica-based RNA purification columns to address the short supply of RNA purification kits for COVID-19 diagnosis.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Oct;48(10):6871-6877. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06688-0. Epub 2021 Sep 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34510319 Free PMC article.
-
DNA purification on homemade silica spin-columns.Anal Biochem. 2003 Oct 1;321(1):135-7. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(03)00403-2. Anal Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12963065 No abstract available.
-
Emulsion PCR made easy.Biotechniques. 2020 Jul;69(1):421-426. doi: 10.2144/btn-2019-0161. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Biotechniques. 2020. PMID: 32338528
-
Regeneration of total RNA purification silica-based columns.Biomed Chromatogr. 2010 Dec;24(12):1263-4. doi: 10.1002/bmc.1418. Biomed Chromatogr. 2010. PMID: 21117284
-
Preparation and application of organic-silica hybrid monolithic capillary columns.Electrophoresis. 2011 Jan;32(1):105-15. doi: 10.1002/elps.201000349. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Electrophoresis. 2011. PMID: 21171117 Review.
Cited by
-
SILEX: a fast and inexpensive high-quality DNA extraction method suitable for multiple sequencing platforms and recalcitrant plant species.Plant Methods. 2020 Aug 10;16:110. doi: 10.1186/s13007-020-00652-y. eCollection 2020. Plant Methods. 2020. PMID: 32793297 Free PMC article.
-
"What I wish I had known before starting my PhD".Anal Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 30;4(1-2):6-12. doi: 10.1002/ansa.202200044. eCollection 2023 Feb. Anal Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 38715583 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing RT-PCR Throughput and Sensitivity through Large-Scale Sample Pooling Using a Nano-Hybrid Membrane.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(10):e2408771. doi: 10.1002/advs.202408771. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39834032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson D, Symons R, Berg P. Biochemical method for inserting new genetic information into DNA of Simian Virus 40: Circular SV40 DNA molecules containing lambda phage genes and the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1972;69:2904–2909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

