GWAS of lifetime cannabis use reveals new risk loci, genetic overlap with psychiatric traits, and a causal influence of schizophrenia
- PMID: 30150663
- PMCID: PMC6386176
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-018-0206-1
GWAS of lifetime cannabis use reveals new risk loci, genetic overlap with psychiatric traits, and a causal influence of schizophrenia
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: GWAS of lifetime cannabis use reveals new risk loci, genetic overlap with psychiatric traits, and a causal effect of schizophrenia liability.Nat Neurosci. 2019 Jul;22(7):1196. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0402-7. Nat Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31168101
Abstract
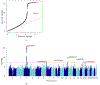
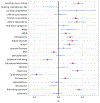
Cannabis use is a heritable trait that has been associated with adverse mental health outcomes. In the largest genome-wide association study (GWAS) for lifetime cannabis use to date (N = 184,765), we identified eight genome-wide significant independent single nucleotide polymorphisms in six regions. All measured genetic variants combined explained 11% of the variance. Gene-based tests revealed 35 significant genes in 16 regions, and S-PrediXcan analyses showed that 21 genes had different expression levels for cannabis users versus nonusers. The strongest finding across the different analyses was CADM2, which has been associated with substance use and risk-taking. Significant genetic correlations were found with 14 of 25 tested substance use and mental health-related traits, including smoking, alcohol use, schizophrenia and risk-taking. Mendelian randomization analysis showed evidence for a causal positive influence of schizophrenia risk on cannabis use. Overall, our study provides new insights into the etiology of cannabis use and its relation with mental health.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
PF, SLE, and members of the 23andMe Research Team are employees of 23andMe Inc.
JARQ was on the speakers’ bureau and/or acted as consultant for Eli-Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, Shire, Lundbeck, Almirall, BRAINGAZE, Sincrolab, and Rubió in the last 5 years. He also received travel awards (air tickets + hotel) for taking part in psychiatric meetings from Janssen-Cilag, Rubió, Shire, and Eli- Lilly. The Department of Psychiatry chaired by him received unrestricted educational and research support from the following pharmaceutical companies in the last 5 years: Eli-Lilly, Lundbeck, Janssen- Cilag, Actelion, Shire, Ferrer, and Rubió.
Figures


References
-
- Hall W & Degenhardt L Adverse health effects of non-medical cannabis use. Lancet (London, England) 374, 1383–1391 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, Neale MC, Jacobson KC, Prescott CA & Kendler KS Illicit drug use and abuse/dependence: modeling of two-stage variables using the CCC approach. Addict Behav 30, 1043–1048 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

