Effects of different principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment on TLR7/NF-κB signaling pathway in influenza virus infected mice
- PMID: 30151032
- PMCID: PMC6102858
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-018-0199-4
Effects of different principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment on TLR7/NF-κB signaling pathway in influenza virus infected mice
Abstract
Background: Influenza virus is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes influenza in humans and animals. About 600 million people around the world suffer from influenza every year. Upon recognizing viral RNA molecules, TLR7 (Toll-like receptor) initiates corresponding immune responses. Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs), including Yinqiao powder, Xinjiaxiangruyin and Guizhi-and-Mahuang decoction, have been extensively applied in clinical treatment of influenza. Although the therapeutic efficacy of TCMs against influenza virus in vivo was reported previously, its underlying mechanisms are not clearly understood. This study aimed to investigate the immunological mechanisms in the treatment of influenza virus infected mice with three Chinese herbal compounds as well as the effect on TLR7/NF-κB signaling pathway during recovery.
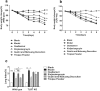
Methods: Wild type and TLR7 KO C57BL/6 mice were infected with influenza virus FM1 and then treated with three TCMs. The physical parameters of mice (body weight and lung index) and the expression levels of components in TLR7/NF-κB signaling pathway were evaluated.
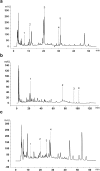
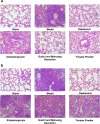
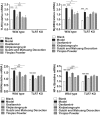
Results: After viral infection, Guizhi-and-Mahuang decoction and Yinqiao powder showed better anti-viral effect under normal condition. Compared to the viral control group, expression levels of TLR7, MyD88, IRAK4 and NF-κB were significantly reduced in all treatment groups. Furthermore, the three TCM treatment groups showed poor therapeutic efficacy and no difference in viral load compared to the viral control group in TLR7 KO mice.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that Guizhi-and-Mahuang decoction and Yinqiao powder might play a crucial role of anti-influenza virus by regulating TLR7/NF-κB signal pathway.
Keywords: Guizhi-and-Mahuang decoction; Influenza virus; TLR7 gene knockout; TLR7/NF-κB signaling pathway; Traditional Chinese Medicine; Xinjiaxiangruyin; Yinqiao powder.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Research progress on the effect of traditional Chinese medicine on the activation of PRRs-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway to inhibit influenza pneumonia.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 7;14:1132388. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1132388. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Xinjiaxiangruyin on the TLR7 pathway in influenza virus-infected lungs of mice housed in a hygrothermal environment.Chin Med. 2019 Sep 27;14:39. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0256-7. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31572491 Free PMC article.
-
Gegen Qinlian Decoction Downregulates the TLR7 Signalling Pathway to Control Influenza A Virus Infection.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109471. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109471. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31707346
-
[Effect of shufeng xuanfei recipe and jiebiao qingli recipe on mRNA and protein expressions of TLR7, MyD88, and NF-kappaB in mice infected with influenza virus].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;33(9):1256-60. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24273985 Chinese.
-
Forsythiaside A improves Influenza A virus infection through TLR7 signaling pathway in the lungs of mice.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jun 22;22(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03644-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35733131 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the effect of traditional Chinese medicine on the activation of PRRs-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway to inhibit influenza pneumonia.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 7;14:1132388. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1132388. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic effect of Yinqiaosan decoction against influenza A virus infection by regulating T cell receptor signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 13;10(16):e36178. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36178. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39253133 Free PMC article.
-
Role of medicinal plants in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 and in the management of post-COVID-19 complications.Phytomedicine. 2022 Apr;98:153930. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153930. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35114450 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Bacillus in fermented soybean foods on human health.Ann Microbiol. 2021;71(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13213-021-01641-9. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Ann Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34305497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD8 T Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-186-5p Elicits Renal Inflammation via Activating Tubular TLR7/8 Signal Axis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Sep;10(25):e2301492. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301492. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37395441 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

