Taurine Attenuates Calpain-2 Induction and a Series of Cell Damage via Suppression of NOX-Derived ROS in ARPE-19 Cells
- PMID: 30151070
- PMCID: PMC6087582
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4596746
Taurine Attenuates Calpain-2 Induction and a Series of Cell Damage via Suppression of NOX-Derived ROS in ARPE-19 Cells
Abstract
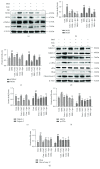
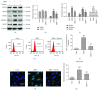
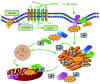
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidases (NOXs) are key transmembrane proteins leading to reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction. However, the detailed roles of NOXs in retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell metabolic stress induced by Earle's balanced salt solution (EBSS) through starvation remain unclear. In this study, we investigated what roles NOXs play in regard to calpain activity, endoplasmic stress (ER), autophagy, and apoptosis during metabolic stress in ARPE-19 cells. We first found that EBSS induced an increase in NOX2, NOX4, p22phox, and NOX5 compared to NOX1. Secondly, suppression of NOXs resulted in reduced ER stress and autophagy, decreased ROS generation, and alleviated cell apoptosis. Thirdly, silencing of NOX4, NOX5, and p22phox resulted in reduced levels of cell damage. However, silencing of NOX1 was unaffected. Finally, taurine critically mediated NOXs in response to EBSS stress. In conclusion, this study demonstrated for the first time that NOX oxidases are the upstream regulators of calpain-2, ER stress, autophagy, and apoptosis. Furthermore, the protective effect of taurine is mediated by the reduction of NOX-derived ROS, leading to sequential suppression of calpain induction, ER stress, autophagy, and apoptosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Starvation-Triggered Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in ARPE-19 Cells by Taurine through Modulating the Expression of Calpain-1 and Calpain-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 14;18(10):2146. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102146. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29036897 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of NADPH Oxidases and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 30;19(12):3824. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123824. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30513656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Release from Endoplasmic Reticulum Involves Calmodulin-Mediated NADPH Oxidase-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 2;20(7):1644. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071644. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30987055 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain Regulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production during Capacitation through the Activation of NOX2 and NOX4.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3980. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043980. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835392 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) and liver fibrosis: A review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2018 Aug;36(6):292-302. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3351. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Biochem Funct. 2018. PMID: 30028028 Review.
Cited by
-
Taurine as a Natural Antioxidant: From Direct Antioxidant Effects to Protective Action in Various Toxicological Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;10(12):1876. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121876. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34942978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy confer protective effects in retinal pigment epithelial cells against sodium iodate-induced cell death.J Biomed Sci. 2019 May 22;26(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0531-z. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 31118030 Free PMC article.
-
Complex interplay between autophagy and oxidative stress in the development of pulmonary disease.Redox Biol. 2020 Sep;36:101679. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101679. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32818797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calpain-2 Facilitates Autophagic/Lysosomal Defects and Apoptosis in ARPE-19 Cells and Rats Induced by Exosomes from RPE Cells under NaIO3 Stimulation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jan 17;2023:3310621. doi: 10.1155/2023/3310621. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36703913 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

