Chemical modulation of transcription factors
- PMID: 30151079
- PMCID: PMC6097187
- DOI: 10.1039/c8md00273h
Chemical modulation of transcription factors
Abstract
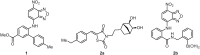
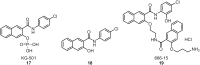
Transcription factors (TFs) constitute a diverse class of sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins, which are key to the modulation of gene expression. TFs have been associated with human diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases, which makes this class of proteins attractive targets for chemical biology and medicinal chemistry research. Since TFs lack a common binding site or structural similarity, the development of small molecules to efficiently modulate TF biology in cells and in vivo is a challenging task. This review highlights various strategies that are currently being explored for the identification and development of modulators of Myc, p53, Stat, Nrf2, CREB, ER, AR, HIF, NF-κB, and BET proteins.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation prediction of antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer based on RNA polymerase II binding data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-S2-S10. Epub 2014 Jan 24. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24564526 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction and Collaboration of SP1, HIF-1, and MYC in Regulating the Expression of Cancer-Related Genes to Further Enhance Anticancer Drug Development.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 17;45(11):9262-9283. doi: 10.3390/cimb45110580. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37998757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inferring transcription factor activity from microarray data reveals novel targets for toxicological investigations.Toxicology. 2017 Aug 15;389:101-107. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28743512
-
Sequence features of DNA binding sites reveal structural class of associated transcription factor.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jan 15;22(2):157-63. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti731. Epub 2005 Nov 2. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16267080
-
Anti-Transcription Factor RNA Aptamers as Potential Therapeutics.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016 Feb;26(1):29-43. doi: 10.1089/nat.2015.0566. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2016. PMID: 26509637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Complex.Molecules. 2020 Dec 18;25(24):6001. doi: 10.3390/molecules25246001. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33352993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CREB in Cancer Therapy: A Key Candidate or One of Many? An Update.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 28;12(11):3166. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113166. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33126560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Homeobox Transcription Factors in a Dimorphic Fungus Talaromyces marneffei and Protein-Protein Interaction Prediction of RfeB.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;10(10):687. doi: 10.3390/jof10100687. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452639 Free PMC article.
-
A protein tertiary structure mimetic modulator of the Hippo signalling pathway.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 27;11(1):5425. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19224-8. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33110077 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repurposing for targeting cyclic nucleotide transporters in acute leukemias - A missed opportunity.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Jan;68:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.02.004. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 32044470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Darnell, Jr. J. E. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:740–749. - PubMed
-
- Overington J. P., Al-Lazikani B., Hopkins A. L. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2006;5:993–996. - PubMed
-
- Plosker G. L. Drugs. 2015;75:297–308. - PubMed
-
- Kuo C. M., Tung T. H., Wang S. H., Chi C. C. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018;32(3):355–362. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

