Diffuse infantile hepatic haemangioma-how to manage an incidental but potentially lethal finding
- PMID: 30151220
- PMCID: PMC6105109
- DOI: 10.1093/omcr/omy054
Diffuse infantile hepatic haemangioma-how to manage an incidental but potentially lethal finding
Abstract
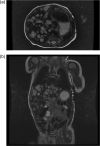
Infantile hepatic haemangioma (IHH) is a rare vascular tumour that is potentially lethal due to its associated complications, including heart failure, hepatic failure, hypothyroidism and abdominal compartment syndrome. The authors report a case of an asymptomatic diffuse IHH in a newborn male, which was presented as an incidental finding at the time that the patient was diagnosed with pyloric stenosis. The patient was treated with increasing doses of propranolol that were well tolerated. With the regression of the IHH by the time that the patient reached one year of age, there was a significant imagiologic improvement. Because there is no consensus on the optimal approach for the treatment of liver tumours in newborns, it is important to adopt a systematic approach. After the diagnosis of diffuse IHH has been established, the decision to initiate treatment and the therapeutic of choice is often controversial. Regular follow-up is recommended to monitor possible complications.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of propranolol treatment in infantile hepatic haemangioma.J Paediatr Child Health. 2019 Oct;55(10):1194-1200. doi: 10.1111/jpc.14375. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Paediatr Child Health. 2019. PMID: 30628130
-
Resolution of Consumptive Hypothyroidism Secondary to Infantile Hepatic Hemangiomatosis with a Combination of Propranolol and Levothyroxine.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2018 Jul 31;10(3):294-298. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.4865. Epub 2018 Feb 28. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29537380 Free PMC article.
-
Propranolol Monotherapy in Multifocal/Diffuse Infantile Hepatic Hemangiomas in Indian Children: A Case Series.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023 Jul-Aug;13(4):707-712. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.02.005. Epub 2023 Feb 15. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37440944 Free PMC article.
-
Infantile hepatic hemangiomas: looking backwards and forwards.Precis Clin Med. 2022 Feb 11;5(1):pbac006. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbac006. eCollection 2022 Mar. Precis Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35692445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
History of the infantile hepatic hemangioma: From imaging to generating a differential diagnosis.World J Clin Pediatr. 2016 Aug 8;5(3):273-80. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v5.i3.273. eCollection 2016 Aug 8. World J Clin Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27610342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pediatric Primary Hepatic Tumors: Diagnostic Considerations.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;11(2):333. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11020333. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670452 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Christison-Lagay ER, Burrows PE, Alomari A, Duboi J, Kozakewic HP, Lane TS, et al. . Hepatic hemangiomas: subtype classification and development of a clinical practice algorithm and registry. J Pediatr Surg 2007;42:62–7. - PubMed
-
- Kulungowski AM, Alomarib AI, Chawlaa A, Christison-Lagaya ER, Fishmana SJ. Lessons from a liver hemangioma registry: subtype classification. J Pediatr Surg 2012;47:165–70. - PubMed
-
- Huang SA, Tu HM, Harney JW, Venihaki M, Butte AJ, Kozakewic HPW, et al. . Severe hypothyroidism caused by type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase in infantile hemangiomas. N Engl J Med 2000;343:185–9. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves C, Lobo L, Anjos R, Salgueiro C, Lopes AI. Hemangioma Hepático Infantil Gigante: Que Opções Terapêuticas? Acta Med Port 2013;26:750–4. - PubMed
-
- Araújo AR, Maciel I, Costa JC, Vieira A, Enes C, Silva EN. Hemangioendotelioma hepático infantil. Un caso multifocal y bilobular, asintomático, con regresión espontánea. An Pediatr (Barc) 2008;68:507–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

