Rapid, simple, and clinically applicable high-performance liquid chromatography method for clinical determination of plasma colistin concentrations
- PMID: 30151222
- PMCID: PMC6100703
- DOI: 10.1186/s40780-018-0119-x
Rapid, simple, and clinically applicable high-performance liquid chromatography method for clinical determination of plasma colistin concentrations
Abstract
Background: Since both the antibacterial effects and common adverse effects of colistin are concentration-dependent, determination of the most appropriate dosage regimen and administration method for colistin therapy is essential to ensure its efficacy and safety. We aimed to establish a rapid and simple high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-based system for the clinical determination of colistin serum concentrations.
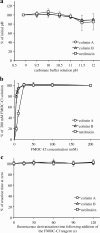
Methods: Extraction using a solid-phase C18 cartridge, derivatisation with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate, and elution with a short reversed-phase Cl8 column effectively separated colistin from an internal standard. The HPLC apparatus and conditions were as follows: analytical column, Hydrosphere C18; sample injection volume, 50 μL; column temperature, 40 °C; detector, Shimadzu RF-5300 fluorescence spectrophotometer (excitation wavelength, 260 nm; emission wavelength, 315 nm); mobile phase, acetonitrile/tetrahydrofuran/distilled water (50,14,20, v/v/v); flow-rate, 1.6 mL/min.
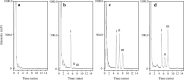
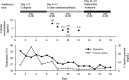
Results: The calibration curves obtained for colistin were linear in the concentration range of 0.10-8.0 μg/mL. The regression equation was y = 0.6496× - 0.0141 (r2 = 0.9999). The limit of detection was ~ 0.025 μg/mL, and the assay intra- and inter-day precisions were 0.87-3.74% and 1.97-6.17%, respectively. The analytical peaks of colistin A, colistin B, and the internal standard were resolved with adequate peak symmetries, and their retention times were approximately 8.2, 6.8, and 5.4 min, respectively. Furthermore, the assay was successfully applied to quantify the plasma colistin levels of a haemodialysis patient.
Conclusion: The assay is a simple, rapid, accurate, selective, clinically applicable HPLC-based method for the quantification of colistin in human plasma.
Keywords: 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate; Colistin; Fluorescence detection; Haemodialysis; High-performance liquid chromatography; Therapeutic drug monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Toho University Omori Medical Center (Approval Number M17280).Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Koyama Y, Kurosasa A, Tsuchiya A, Takakuta K. A new antibiotic “colistin” produced by spore-forming soil bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1950;3:457–458.
-
- Berlana D, Llop JM, Fort E, Badia MB, Jodar R. Use of colistin in the treatment of multiple-drug-resistant gram-negative infections. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005;62:39–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

