Quantitative Proteomics of Xenopus Embryos I, Sample Preparation
- PMID: 30151767
- PMCID: PMC6564683
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8784-9_13
Quantitative Proteomics of Xenopus Embryos I, Sample Preparation
Abstract
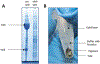
Xenopus oocytes and embryos are model systems optimally suited for quantitative proteomics. This is due to the availability of large amount of protein material and the ease of physical manipulation. Furthermore, facile in vitro fertilization provides superbly synchronized embryos for cell cycle and developmental stages. Here, we detail protocols developed over the last few years for sample preparation of multiplexed proteomics with TMT-tags followed by quantitative mass spectrometry analysis using the MultiNotch MS3 approach. In this approach, each condition is barcoded with an isobaric tag at the peptide level. After barcoding, samples are combined and the relative abundance of ~100,000 peptides is quantified on a mass spectrometer. High reproducibility of the sample preparation process prior to peptides being tagged and combined is of upmost importance for obtaining unbiased data. Otherwise, differences in sample handling can inadvertently appear as biological changes. We detail and exemplify the application of our sample workflow on an embryonic time-series of ten developmental stages of Xenopus laevis embryos ranging from the egg to stage 35 (just before hatching). Our accompanying paper (Chapter 14 ) details a bioinformatics pipeline to analyze the quality of the given sample preparation and strategies to convert spectra of X. laevis peptides into biologically interpretable data.
Keywords: Development; Mass spectrometry; Multiplexing; Protein dynamics; Proteomics; Sample preparation; TMT; Xenopus laevis; Yolk.
Figures



References
-
- Swammerdam J (1737) Bibilia Naturae; Sive historia insectorum, in classes certas redact 2
-
- Prevost JL, Dumas J-B (1824) Nouvelle théorie de la génération. Ann Sci Nat 2
-
- Gurdon JB, Elsdale TR, Fischberg M (1958) Sexually mature individuals of Xenopus laevis from the transplantation of single somatic nuclei. Nature 182(4627):64–65 - PubMed
-
- Paine PL, Moore LC, Horowitz SB (1975) Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature 254(5496):109–114 - PubMed
-
- Session AM, Uno Y, Kwon T, Chapman JA, Toyoda A, Takahashi S, Fukui A, Hikosaka A, Suzuki A, Kondo M, van Heeringen SJ, Quigley I, Heinz S, Ogino H, Ochi H, Hellsten U, Lyons JB, Simakov O, Putnam N, Stites J, Kuroki Y, Tanaka T, Michiue T, Watanabe M, Bogdanovic O, Lister R, Georgiou G, Paranjpe SS, van Kruijsbergen I, Shu S, Carlson J, Kinoshita T, Ohta Y, Mawaribuchi S, Jenkins J, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Mitros T, Mozaffari SV, Suzuki Y, Haramoto Y, Yamamoto TS, Takagi C, Heald R, Miller K, Haudenschild C, Kitzman J, Nakayama T, Izutsu Y, Robert J, Fortriede J, Burns K, Lotay V, Karimi K, Yasuoka Y, Dichmann DS, Flajnik MF, Houston DW, Shendure J, DuPasquier L, Vize PD, Zorn AM, Ito M, Marcotte EM, Wallingford JB, Ito Y, Asashima M, Ueno N, Matsuda Y, Veenstra GJ, Fujiyama A, Harland RM, Taira M, Rokhsar DS (2016) Genome evolution in the allotetraploid frog Xenopus laevis. Nature 538(7625):336–343. 10.1038/nature19840 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

