Protein phosphatase 2A regulates the p38 signaling pathway to affect the migration of astrocytes
- PMID: 30152844
- PMCID: PMC6172367
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9425
Protein phosphatase 2A regulates the p38 signaling pathway to affect the migration of astrocytes
Abstract
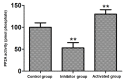
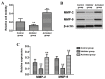
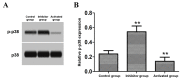
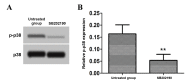
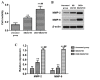
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect and mechanism of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) on the migration of astrocytes. The primary astrocytes of neonatal mice were isolated and cultured in vitro, and treated with the PP2A activator D‑erythro‑sphingosine (DES) (activated group) or inhibitor okadaic acid (inhibitory group). The control group was treated with equal amounts of dimethyl sulfoxide. The activity of PP2A in the cells was detected using a commercial kit and the migration of cells was investigated using a Transwell migration assay. The protein expression of p38, phosphorylated (p)‑p38, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)‑2 and MMP‑9 was detected by western blotting. Cell migration and the protein expression of p38, p‑p38, MMP‑2 and MMP‑9 was also determined following treatment of astrocytes with the p38 signaling pathway inhibitor SB202190 with or without the PP2A activator DES. The results demonstrated that the activity of PP2A in the PP2A inhibitory group was significantly decreased compared with the control group, while that of the PP2A‑activated cells was significantly increased compared with the control. The protein levels of MMP‑2 and MMP‑9 in the PP2A inhibitory group astrocytes were significantly decreased compared with the control group, while PP2A‑activated astrocytes exhibited significantly increased levels of these proteins. By contrast, the p‑p38 level in PP2A inhibitory group astrocytes was significantly increased compared with the control group, while astrocytes in the activated group exhibited significantly lower levels compared with the control group. Furthermore, the cell migration ability, and MMP‑2 and MMP‑9 protein levels, of astrocytes that received combined treatment with SB202190 and the PP2A activator DES were significantly increased compared with the levels in astrocytes treated with SB202190 alone. The results of the current study indicate that PP2A may negatively regulate the p38 signaling pathway to promote astrocyte migration.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Y, Zeng X, Hui Y, Zhu C, Wu J, Taylor DH, Ji J, Fan W, Huang Z, Hu J. Activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors protects astrocytes against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: Implications for Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology. 2015;91:87–96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.11.028. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

