Mammalian DNA methyltransferases: new discoveries and open questions
- PMID: 30154093
- PMCID: PMC6581191
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20170574
Mammalian DNA methyltransferases: new discoveries and open questions
Erratum in
-
Correction: Mammalian DNA methyltransferases: new discoveries and open questions.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Jun 28;47(3):959. doi: 10.1042/BST-2017-0574C_COR. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31235548 No abstract available.
Abstract
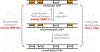
As part of the epigenetic network, DNA methylation is a major regulator of chromatin structure and function. In mammals, it mainly occurs at palindromic CpG sites, but asymmetric methylation at non-CpG sites is also observed. Three enzymes are involved in the generation and maintenance of DNA methylation patterns. DNMT1 has high preference for hemimethylated CpG sites, and DNMT3A and DNMT3B equally methylate unmethylated and hemimethylated DNA, and also introduce non-CpG methylation. Here, we review recent observations and novel insights into the structure and function of mammalian DNMTs (DNA methyltransferases), including new structures of DNMT1 and DNMT3A, data on their mechanism, regulation by post-translational modifications and on the function of DNMTs in cells. In addition, we present news findings regarding the allosteric regulation and targeting of DNMTs by chromatin modifications and chromatin proteins. In combination, the recent publications summarized here impressively illustrate the intensity of ongoing research in this field. They provide a deeper understanding of key mechanistic properties of DNMTs, but they also document still unsolved issues, which need to be addressed in future research.
Keywords: DNA methylation; DNA methyltransferases; enzymology; molecular epigenetics.
© 2018 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

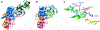
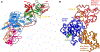
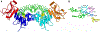
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

