Evaluation and management of adult idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- PMID: 30154235
- PMCID: PMC6252364
- DOI: 10.1136/practneurol-2018-002009
Evaluation and management of adult idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Abstract
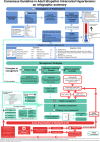
This paper summarises the first consensus guidelines for idiopathic intracranial hypertension as an infographic. Following a systematic literature review, a multidisciplinary specialist interest group met and established questions relating to population, interventions, controls and outcomes (PICO). A survey was sent to doctors who manage idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) regularly. Statements were reviewed by national professional bodies, specifically the Association of British Neurologists, British Association for the Study of Headache, the Society of British Neurological Surgeons and the Royal College of Ophthalmologists and by international experts. Key areas are represented based on the guideline, namely: (1) investigation of papilloedema and diagnosis of IIH; (2) management strategies; and (3) investigation and management of acute exacerbation of headache in established IIH. We present an infographic as an aide-mémoire of the first consensus guidelines for IIH.
Keywords: benign intracran hyp; headache; idiopathic intracranial hypertension; neuroophthalmology; papilloedema.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2018. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous