Structural analysis reveals pathomechanisms associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum-causing mutations in the ABCC6 transporter
- PMID: 30154241
- PMCID: PMC6187630
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004806
Structural analysis reveals pathomechanisms associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum-causing mutations in the ABCC6 transporter
Abstract
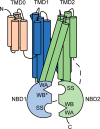
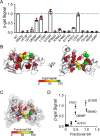
Mutations in ABC subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) transporter are associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), a disease resulting in ectopic mineralization and affecting multiple tissues. A growing number of mutations have been identified in individuals with PXE. For most of these variants, no mechanistic information is available regarding their role in normal and pathophysiologies. To assess how PXE-associated mutations alter ABCC6 biosynthesis and structure, we biophysically and biochemically evaluated the N-terminal nucleotide-binding domain. A high-resolution X-ray structure of nucleotide-binding domain 1 (NBD1) of human ABCC6 was obtained at 2.3 Å that provided a template on which to evaluate PXE-causing mutations. Biochemical analysis of mutations in this domain indicated that multiple PXE-causing mutations altered its structural properties. Analyses of the full-length protein revealed a strong correlation between the alterations in NBD properties and the processing and expression of ABCC6. These results suggest that a significant fraction of PXE-associated mutations located in NBD1 causes changes in its structural properties and that these mutation-induced alterations directly affect the maturation of the full-length ABCC6 protein.
Keywords: ABC transporter; ABCC6; X-ray crystallography; connective tissue; connective tissue disorder; elastic fiber; glycoprotein biosynthesis; membrane protein; protein folding; protein misfolding; protein stability; protein structure; pseudoxanthoma elasticum.
© 2018 Ran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures





References
-
- Le Saux O., Urban Z., Tschuch C., Csiszar K., Bacchelli B., Quaglino D., Pasquali-Ronchetti I., Pope F. M., Richards A., Terry S., Bercovitch L., de Paepe A., and Boyd C. D. (2000) Mutations in a gene encoding an ABC transporter cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Nat. Genet. 25, 223–227 10.1038/76102 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jansen R. S., Küçükosmanoglu A., de Haas M., Sapthu S., Otero J. A., Hegman I. E., Bergen A. A., Gorgels T. G., Borst P., and van de Wetering K. (2013) ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 20206–20211 10.1073/pnas.1319582110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

