Analysis of Bacterial Communities in Partial Nitritation and Conventional Nitrification Systems for Nitrogen Removal
- PMID: 30154517
- PMCID: PMC6113234
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30532-4
Analysis of Bacterial Communities in Partial Nitritation and Conventional Nitrification Systems for Nitrogen Removal
Abstract
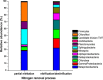
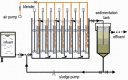
This work studied the microbial community in partial nitritation and complete nitrification processes, which were applied to treat the low Carbon Nitrogen ratio wastewater. The phospholipid fatty acid and quantitative PCR analysis showed that the sludge circulating ratio of 75% resulted in a good microbial growth and a higher abundance of ammonia oxidizing bacteria relative to the nitrite oxidizing bacteria. The Betaproteobacteria were observed to compose the most abundant sludge bacterial groups in the two processes, based on phylogenetic analysis. The phylogenetic analysis of both 16S rRNA and amoA gene indicated that the Nitrosomonas sp. were the dominant ammonia oxidizing bacteria in the partial nitritation process. The relative abundance of nitrite oxidizing bacteria, such as Nitrobacter sp. and Nitrospira sp., were significantly lower in the partial nitritation system over the complete nitrification system. The abundance of Planctomycetes was higher in the partial nitritation process, indicating the anammox reaction occurred in the partial nitritation system. These results suggested the nitrite accumulation rate of circulating ratios 75% was the highest, with an average of 92%,and a possibility to treat the low Carbon Nitrogen ratio wastewater using the partial nitritation/anammox process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[Running Condition and Bacterial Community Associated with the Partial Nitritation System].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2015 Apr;36(4):1399-405. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2015. PMID: 26164918 Chinese.
-
Population dynamics of nitrifying bacteria for nitritation achieved in Johannesburg (JHB) process treating municipal wastewater.Bioresour Technol. 2014 Jun;162:30-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.102. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Bioresour Technol. 2014. PMID: 24736209
-
One-stage partial nitritation and anammox in membrane bioreactor.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Jun;23(11):11149-11162. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6309-x. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26916267
-
A New Perspective on Microbes Formerly Known as Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria.Trends Microbiol. 2016 Sep;24(9):699-712. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Trends Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27283264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organic carbon bioavailability: Is it a good driver to choose the best biological nitrogen removal process?Sci Total Environ. 2021 Sep 10;786:147390. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147390. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33964770 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Soil Microbial Community Structures in Rhizosphere of Two Texture-Differentiated Lotus Root Varieties.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 10;13(7):1637. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071637. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732146 Free PMC article.
-
Achieving Partial Nitrification-Anammox Process Dependent on Microalgal-Bacterial Consortia in a Photosequencing Batch Reactor.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 18;10:851800. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.851800. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35372325 Free PMC article.
-
A critical review for removal of pre- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from landfill leachate: possible solutions with biological nitrogen removal and anammox systems.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 14;41(8):311. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04529-x. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40804600 Review.
References
-
- Nielsen LP. Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 1992;9:357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.1992.tb01771.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
- 500 thousand yuan/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

