Gait training using a stationary, one-leg gait exercise assist robot for chronic stroke hemiplegia: a case report
- PMID: 30154598
- PMCID: PMC6110205
- DOI: 10.1589/jpts.30.1046
Gait training using a stationary, one-leg gait exercise assist robot for chronic stroke hemiplegia: a case report
Abstract
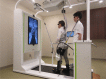
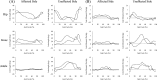
[Purpose] The Gait Exercise Assist Robot (GEAR) is a stationary, one-leg robot for gait training. The purpose of this case study was to evaluate the efficacy of rehabilitation using GEAR training for chronic stroke hemiplegia. [Participant and Methods] The participant was a 66-year-old male stroke survivor with left hemiparesis due to a right putaminal hemorrhage. He could walk slowly under supervision, although his gait had a constant forward trunk lean, with flexed knee, and a lack of hip extension movement on the affected side. Gait training using GEAR and physical therapy were performed for 14 days. Under both training conditions, the physical therapist made the participant conscious of extension movement of the hip joint in the affected-side stance phase. The robotic assistance was adjusted to maximize voluntary movement while observing gait. Physical function and gait ability parameters were evaluated before and after training. [Results] After training, extension motion of the hip joint increased in the affected-side stance phase, and body weight was transferred smoothly onto the affected-side limb, leading to an improvement in gait speed. [Conclusion] Gait training using GEAR and physical therapy may improve gait pattern and speed in patients with chronic stroke hemiplegia.
Keywords: Chronic stroke hemiplegia; Gait training; Robot.
Figures
References
-
- Calabrò RS, Cacciola A, Bertè F, et al. : Robotic gait rehabilitation and substitution devices in neurological disorders: where are we now? Neurol Sci, 2016, 37: 503–514. - PubMed
-
- Colombo G, Joerg M, Schreier R, et al. : Treadmill training of paraplegic patients using a robotic orthosis. J Rehabil Res Dev, 2000, 37: 693–700. - PubMed
-
- Hesse S, Uhlenbrock D, Sarkodie-Gyan T: Gait pattern of severely disabled hemiparetic subjects on a new controlled gait trainer as compared to assisted treadmill walking with partial body weight support. Clin Rehabil, 1999, 13: 401–410. - PubMed
-
- Peurala SH, Tarkka IM, Pitkänen K, et al. : The effectiveness of body weight-supported gait training and floor walking in patients with chronic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2005, 86: 1557–1564. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
