Recent advances in "smart" delivery systems for extended drug release in cancer therapy
- PMID: 30154657
- PMCID: PMC6108334
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S168053
Recent advances in "smart" delivery systems for extended drug release in cancer therapy
Abstract
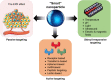
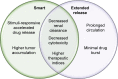
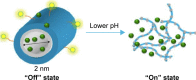
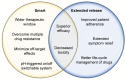
Advances in nanomedicine have become indispensable for targeted drug delivery, early detection, and increasingly personalized approaches to cancer treatment. Nanoparticle-based drug-delivery systems have overcome some of the limitations associated with traditional cancer-therapy administration, such as reduced drug solubility, chemoresistance, systemic toxicity, narrow therapeutic indices, and poor oral bioavailability. Advances in the field of nanomedicine include "smart" drug delivery, or multiple levels of targeting, and extended-release drug-delivery systems that provide additional methods of overcoming these limitations. More recently, the idea of combining smart drug delivery with extended-release has emerged in hopes of developing highly efficient nanoparticles with improved delivery, bioavailability, and safety profiles. Although functionalized and extended-release drug-delivery systems have been studied extensively, there remain gaps in the literature concerning their application in cancer treatment. We aim to provide an overview of smart and extended-release drug-delivery systems for the delivery of cancer therapies, as well as to introduce innovative advancements in nanoparticle design incorporating these principles. With the growing need for increasingly personalized medicine in cancer treatment, smart extended-release nanoparticles have the potential to enhance chemotherapy delivery, patient adherence, and treatment outcomes in cancer patients.
Keywords: extended drug release; nanomedicine; personalized medicine; smart delivery systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure This work was supported in part by grants to MRS from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and private-sector cancer funding from the Josefowitz family and Encyt Technologies Inc to MRS. RVK is a recipient of the Queen’s Graduate Award (QGA). BQ is a recipient of the QGA and part of the 2017 Terry Fox Research Institute Transdisciplinary Training Program in Cancer Research. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Hare JI, Lammers T, Ashford MB, Puri S, Storm G, Barry ST. Challenges and strategies in anti-cancer nanomedicine development: an industry perspective. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;108:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Lammers T. Improving the efficacy of combined modality anticancer therapy using HPMA copolymer-based nanomedicine formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(2):203–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

