Hypoglycaemic activity of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice through ameliorating metabolic function and regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- PMID: 30154901
- PMCID: PMC6111351
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2016.63285
Hypoglycaemic activity of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice through ameliorating metabolic function and regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus is characterized by hyperglycaemia causing changes in plasma lipoproteins, which leads to insulin resistance, secretion defects or both. The present study aimed to evaluate the ability of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxy-cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (DMDD) isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. roots to lower hyperglycaemia and to investigate its potential mechanism in diabetic mice.
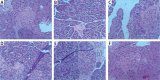
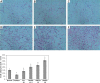
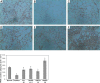
Material and methods: DMDD was isolated using a column chromatographic technique. Experimental mice were fed with a high-fat diet for a month and were intravenously injected with streptozotocin (80 mg/kg, single dose). Diabetic mice were orally administered DMDD (12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg) and 50 mg/kg pioglitazone for 15 days. Fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting blood insulin (FINS), pancreatic insulin content, interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), as well as serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) and free fatty acid (FFA) were determined. Adipose tissue was assessed by histological examination, immunohistochemistry, western blot and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction methods.
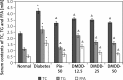
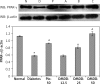
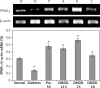
Results: DMDD significantly increased the insulin level (all p < 0.05). In contrast, FBG, IL-6, TNF-α, TC, TG and FFA were significantly decreased (all p < 0.05). However, DMDD induced the activation of adipocyte peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ), confirmed by increased protein and mRNA expression of PPAR-γ.
Conclusions: DMDD possessed hypoglycaemic activity due to its potential mechanism involving PPARγ-mediated adipocyte endocrine regulation.
Keywords: Averrhoa carambola L.; adipocyte; diabetes; endocrine; mechanism; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(suppl 1):S43–8. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation Type 1 diabetes: a very special issue. Diabetes Voice. 2011;56:4–49.
-
- Sun K, Li F, Qi Y, et al. Sex difference in the association between habitual daytime napping and prevalence of diabetes: a population-based study. Endocrine. 2016;52:263–70. - PubMed
-
- Wong KC, Wang Z. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus of Chinese populations in mainland China, Hongkong, and Taiwan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;73:126–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
