Large-Deformation Image Registration of CT-TEE for Surgical Navigation of Congenital Heart Disease
- PMID: 30154912
- PMCID: PMC6091287
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4687376
Large-Deformation Image Registration of CT-TEE for Surgical Navigation of Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract
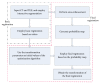
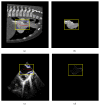
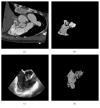
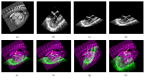
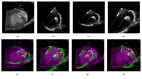
The surgical treatment of congenital heart disease requires navigational assistance with transesophageal echocardiography (TEE); however, TEE images are often difficult to interpret and provide very limited anatomical information. Registering preoperative CT images to intraoperative TEE images provides surgeons with richer and more useful anatomical information. Yet, CT and TEE images differ substantially in terms of scale and geometry. In the present research, we propose a novel method for the registration of CT and TEE images for navigation during surgical repair of large defects in patients with congenital heart disease. Valve data was used for the coarse registration to determine the basic location. This was followed by the use of an enhanced probability model map to overcome gray-level differences between the two imaging modalities. Finally, the rapid optimization of mutual information was achieved by migrating parameters. This method was tested on a dataset of 240 images from 12 infant, children (≤ 3 years old), and adult patients with congenital heart disease. Compared to the "bronze standard" registration, the proposed method was more accurate with an average Dice coefficient of 0.91 and an average root mean square of target registration error of 1.2655 mm.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CT-TEE Image Registration for Surgical Navigation of Congenital Heart Disease Based on a Cycle Adversarial Network.Comput Math Methods Med. 2020 Jul 2;2020:4942121. doi: 10.1155/2020/4942121. eCollection 2020. Comput Math Methods Med. 2020. PMID: 32802148 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of transesophageal echocardiography in assessing congenital heart disease: our experience.Congenit Heart Dis. 2014 Jul-Aug;9(4):300-6. doi: 10.1111/chd.12139. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Congenit Heart Dis. 2014. PMID: 24102771
-
Utility of intraoperative transesophageal echocardiogram in congenital heart disease.J Med Assoc Thai. 2000 Nov;83 Suppl 2:S46-53. J Med Assoc Thai. 2000. PMID: 11194021
-
Role of transesophageal echocardiography in the management of pediatric patients with congenital heart disease.Paediatr Anaesth. 2011 May;21(5):479-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2011.03570.x. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011. PMID: 21481076 Review.
-
Transesophageal echocardiography in congenital heart disease in the adult.Cardiol Clin. 1993 Aug;11(3):505-20. Cardiol Clin. 1993. PMID: 8402777 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an Innovative Pipeline With Fusion, Digital Planning, and Three-Dimensional Printing to Improve Mitral Valve Interventional Care.Echocardiography. 2025 May;42(5):e70184. doi: 10.1111/echo.70184. Echocardiography. 2025. PMID: 40391921 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitude and practice of pediatric healthcare staff towards the therapy for patients with congenital heart disease.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Nov 14;24(1):1312. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06305-1. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39543572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manjunath B. S., Shekhar C., Chellappa R. A new approach to image feature detection with applications. Pattern Recognition. 1996;29(4):627–640. doi: 10.1016/0031-3203(95)00115-8. - DOI
-
- Fonseca L. M. G., Costa M. H. M. Automatic registration of satellite images. Proceedings of the 1997 10th Brazilian Symposium of Computer Graphic and Image Processing, SIBGRAPI 97; October 1997; Campos do Jordao, Brazil. pp. 219–226.
-
- Feng Y., Schlichting A., Brenner C. 3D Feature point extraction from lidar data using a neural network. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences - ISPRS Archives 41. 2016;XLI-B1:563–569. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLI-B1-563-2016. - DOI
-
- Cheng Y., Dubois T. Object Recognition by Using Multi-level Feature Point Extraction. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017
-
- Chen W. Y., Pan T. F., Chen L. G. A spatial first 3-D XYT feature point extraction algorithm for efficient human action recognition. Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Taiwan (ICCE-TW); May 2014; Taipei, Taiwan. pp. 101–102. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

