Essential role of hydride ion in ruthenium-based ammonia synthesis catalysts
- PMID: 30155046
- PMCID: PMC6013784
- DOI: 10.1039/c6sc00767h
Essential role of hydride ion in ruthenium-based ammonia synthesis catalysts
Erratum in
-
Correction: Essential role of hydride ion in ruthenium-based ammonia synthesis catalysts.Chem Sci. 2016 Aug 1;7(8):5596. doi: 10.1039/c6sc90039a. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 30124680 Free PMC article.
Abstract
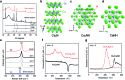
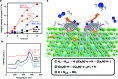
The efficient reduction of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia under low pressure and temperature conditions has been a challenge in meeting the rapidly increasing demand for fertilizers and hydrogen storage. Here, we report that Ca2N:e-, a two-dimensional electride, combined with ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru/Ca2N:e-) exhibits efficient and stable catalytic activity down to 200 °C. This catalytic performance is due to [Ca2N]+·e1-x-H x- formed by a reversible reaction of an anionic electron with hydrogen (Ca2N:e- + xH ↔ [Ca2N]+·e1-x-H x-) during ammonia synthesis. The simplest hydride, CaH2, with Ru also exhibits catalytic performance comparable to Ru/Ca2N:e-. The resultant electrons in these hydrides have a low work function of 2.3 eV, which facilitates the cleavage of N2 molecules. The smooth reversible exchangeability between anionic electrons and H- ions in hydrides at low temperatures suppresses hydrogen poisoning of the Ru surfaces. The present work demonstrates the high potential of metal hydrides as efficient promoters for low-temperature ammonia synthesis.
Figures


References
-
- Gambarotta S., Scott J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004;43:5298–5308. - PubMed
-
- Mittasch A. Adv. Catal. 1950;2:81–104.
-
- Satyapal S., Petrovic J., Read C., Thomas G., Ordaz G. Catal. Today. 2007;120:246–256.
-
- Pool J. A., Lobkovsky E., Chirik P. J. Nature. 2004;427:527–530. - PubMed
-
- Arashiba K., Miyake Y., Nishibayashi Y. Nat. Chem. 2011;3:120–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

