Ultra-sensitive detection of protein biomarkers for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30155210
- PMCID: PMC6094176
- DOI: 10.1039/c6sc05615f
Ultra-sensitive detection of protein biomarkers for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
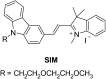
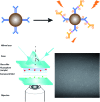
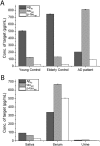
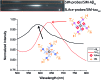
Beta amyloid peptide, tau, and phosphorylated tau are well recognized as promising biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this work, we developed a direct, versatile, and ultrasensitive multiplex assay for the quantification of trace amounts of these protein biomarkers for AD in different types of biological fluids including cerebrospinal fluid, serum, saliva, and urine. The detection assay is based on the immunoreaction between the target proteins and their corresponding pair of antibodies followed by fluorescence labelling with a newly developed indolium-based turn-on fluorophore, namely SIM. SIM was tailor-made as a reporter to provide a high signal-to-noise ratio for the detection assay. An exceptionally low limit of detection down to the femto-molar level was achieved in this assay with minute consumption of the sample. This versatile detection assay is capable of reliably quantifying not only the target proteins simultaneously from a CSF sample in an hour but also trace amounts of protein biomarkers in saliva and urine. This assay has a high potential to serve as a practical tool for the diagnosis of AD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Highly sensitive quantification of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers by aptamer-assisted amplification.Theranostics. 2019 May 9;9(10):2939-2949. doi: 10.7150/thno.29232. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31244934 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and multiplex quantification of protein biomarkers in serum samples using an immuno-magnetic platform.Chem Sci. 2016 Apr 21;7(4):2695-2700. doi: 10.1039/c5sc04115e. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 28660042 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the development paradigm of biosample-based biosensors for early ultrasensitive detection of alzheimer's disease.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Mar 9;19(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00814-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33750392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta-amyloid (1-42), phosphorylated tau (ptau-181) and total Tau protein in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other dementia at Siriraj Hospital, Thailand.J Med Assoc Thai. 2011 Feb;94 Suppl 1:S77-83. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011. PMID: 21721431
-
Fluid biomarker-based molecular phenotyping of Alzheimer's disease patients in research and clinical settings.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019;168:3-23. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 31699324 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent progress of small-molecule-based theranostic agents in Alzheimer's disease.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Sep 14;14(11):2231-2245. doi: 10.1039/d3md00330b. eCollection 2023 Nov 15. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37974955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Plasma Oligomeric Amyloid β-42 Is Associated with Cognitive Impairments in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;13(1):110. doi: 10.3390/bios13010110. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671945 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobiosensors for Non-Amyloidbeta-Tau Biomarkers as Advanced Reporters of Alzheimer's Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Nov 8;10(11):913. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110913. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33171630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma phosphorylated tau 181 predicts amyloid status and conversion to dementia stage dependent on renal function.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023 Jun;94(6):411-419. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2022-330540. Epub 2023 Apr 3. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37012068 Free PMC article.
-
A novel kit for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease using a fluorescent nanoparticle imaging.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 12;9(1):13184. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49711-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31515517 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

