Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticles for cancer theragnostic applications
- PMID: 30155269
- PMCID: PMC6108142
- DOI: 10.1186/s40824-018-0132-z
Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticles for cancer theragnostic applications
Abstract
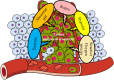
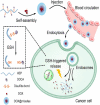
Background: Cancer is one of the deadliest threats to human health. Abnormal physiochemical conditions and dysregulated biosynthetic intermediates in the tumor microenvironment (TME) play a significant role in modulating cancer cells to evade or defend conventional anti-cancer therapy such as surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. One of the most important challenges in the development of anti-tumor therapy is the successful delivery of therapeutic and imaging agents specifically to solid tumors.
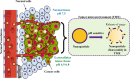
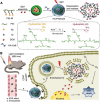
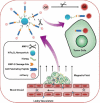
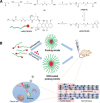
Main body: The recent progresses in development of TME responsive nanoparticles offers promising strategies for combating cancer by making use of the common attributes of tumor such as acidic and hypoxic microenvironments. In this review, we discussed the prominent strategies utilized in the development of tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticles and mode of release of therapeutic cargo.
Conclusion: Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticles offers a universal approach for anti-cancer therapy.
Keywords: Cancer; Hypoxia; Nanoparticle; Redox; Tumor microenvironment; pH.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Enabled Nanotherapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Apr;7(8):e1701156. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201701156. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29283221 Review.
-
Responsive Role of Nanomedicine in the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Drug Resistance.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(29):3335-3355. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220922111336. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36154585 Review.
-
The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 26;6(7):1973-1987. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010. eCollection 2021 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33426371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimuli-responsive nanoassemblies for targeted delivery against tumor and its microenvironment.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022 Sep;1877(5):188779. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188779. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35977690 Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Nanotherapeutics in Targeting Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Dec;126:109-122. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.05.010. Epub 2017 May 13. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28511988 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanovectorization of Prostate Cancer Treatment Strategies: A New Approach to Improved Outcomes.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Apr 21;13(5):591. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050591. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33919150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MnCO3-mineralized polydopamine nanoparticles as an activatable theranostic agent for dual-modality imaging-guided photothermal therapy of cancers.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 21;12(15):6762-6778. doi: 10.7150/thno.77060. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185599 Free PMC article.
-
Alliance with EPR Effect: Combined Strategies to Improve the EPR Effect in the Tumor Microenvironment.Theranostics. 2019 Oct 17;9(26):8073-8090. doi: 10.7150/thno.37198. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31754382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causes, consequences, and therapy of tumors acidosis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019 Jun;38(1-2):205-222. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09792-7. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019. PMID: 30911978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Delivery of Natural Products Through Nanocarriers for Effective Breast Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Literature.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 2;16:7891-7941. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S328135. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34880614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jiang W, von Roemeling CA, Chen YX, Qie YQ, Liu XJ, Chen JZ, Kim BYS. Designing nanomedicine for immuno-oncology. Nat Biomed Eng. 2017;1:0029.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

