New-Onset Diabetes Presenting as Monoballism Secondary to a Mixed Hyperglycemic Crisis
- PMID: 30155384
- PMCID: PMC6110419
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2882
New-Onset Diabetes Presenting as Monoballism Secondary to a Mixed Hyperglycemic Crisis
Abstract
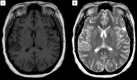
Monoballism secondary to a mixed hyperglycemic crisis is a rare initial symptom of new-onset diabetes, which commonly affects the elderly and Asian women having inadequate glycemic control. In hyperglycemic states, the elevated serum glucose levels raise the viscosity of the blood reducing cerebral perfusion, decreasing gamma-aminobutyric acid levels, the latter being an inhibitory neurotransmitter of thalamocortical stimuli. In this case, we report a previously healthy 41-year-old male who attended the emergency department because of an abrupt onset movement disorder of the left arm, this being compatible with monoballism. He was diagnosed with a mixed hyperglycemic crisis.
Keywords: ballism; hemiballism; hyperglycemic crisis; hyperkinetic; monoballism; movement disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Movement disorders caused by medical disease. Barton B, Zauber S, Goetz C. Semin Neurol. 2009;29:97–110. - PubMed
-
- Non-ketotic hyperglycemic chorea-hemiballismus mimicking basal ganglia hemorrhage. Wilson TJ, Than KD, Stetler WR, Heth JA. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:1560–1561. - PubMed
-
- Some observations on hemiballismus. Bedwell SF. Neurology. 1960;10:619–622. - PubMed
-
- Hyperglycemia-induced hemiballismus hemichorea: a case report and brief review of the literature. Narayanan S. J Emerg Med. 2012;43:442–444. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources