A comprehensive analysis of auditory event-related potentials and network oscillations in an NMDA receptor antagonist mouse model using a novel wireless recording technology
- PMID: 30155997
- PMCID: PMC6113138
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13782
A comprehensive analysis of auditory event-related potentials and network oscillations in an NMDA receptor antagonist mouse model using a novel wireless recording technology
Abstract
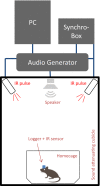
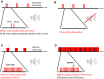
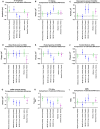
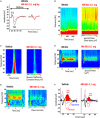
There is growing evidence that impaired sensory processing significantly contributes to cognitive deficits found in schizophrenia. Electroencephalography (EEG) has become an important preclinical and clinical technique to investigate the underlying mechanisms of neurophysiological dysfunctions in psychiatric disorders. Patients with schizophrenia show marked deficits in auditory event-related potentials (ERP), the detection of deviant auditory stimuli (mismatch negativity, MMN), the generation and synchronization of 40 Hz gamma oscillations in response to steady-state auditory stimulation (ASSR) and reduced auditory-evoked oscillation in the gamma range. Due to a novel data-logging technology (Neurologger, TSE Systems), it is now possible to record wireless EEG data in awake, free-moving small rodents without any restrictions due to size of the device or attached cables. Recently, a new version of the Neurologger was released with improved performance to record time-locked event-related EEG signals. In this study, we were able to show in mice that pharmacological intervention with the NMDA receptor antagonists Ketamine and MK-801 can impair a comprehensive selection of EEG/ERP readouts (ERP N1 amplitude, 40 Hz ASSR, basal and evoked gamma oscillation, MMN) and therefore mimic the EEG deficits observed in patients with schizophrenia. Our data support the translational value of NMDA receptor antagonists as a model for preclinical evaluation of sensory processing deficits relevant to schizophrenia. Further, the new Neurologger system is a suitable device for wireless recording of clinically relevant EEG biomarkers in freely moving mice and a robust translational tool to investigate novel therapeutic approaches regarding sensory processing deficits related to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.
Keywords: Animal model; NMDA receptor antagonist; event-related potentials; gamma oscillation; schizophrenia; translational biomarker.
© 2018 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of NMDA and GABA-A Receptor Antagonism on Auditory Steady-State Synchronization in Awake Behaving Rats.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Jan 2;18(7):pyu118. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu118. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25556198 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of traxoprodil and S-ketamine on quantitative EEG and auditory event-related potentials as translational biomarkers in preclinical trials in rats and mice.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Jul;171:108072. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108072. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32243874
-
N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor antagonist-induced frequency oscillations in mice recreate pattern of electrophysiological deficits in schizophrenia.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 23;158(2):705-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.10.031. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19015010
-
Neurophysiological models for new treatment development in schizophrenia: early sensory approaches.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 May;1344:92-104. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12689. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 25721890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal imbalance of excitation and inhibition in schizophrenia: a scoping review of gamma-band ASSR findings.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022 Dec;76(12):610-619. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13472. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36069299
Cited by
-
Differential Effects of Clozapine and Haloperidol on the 40 Hz Auditory Steady State Response-mediated Phase Resetting in the Prefrontal Cortex of the Female Sprague Dawley Rat.Schizophr Bull. 2023 May 3;49(3):581-591. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbac203. Schizophr Bull. 2023. PMID: 36691888 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the mGlu2/3 receptor agonist LY379268 on two models of disturbed auditory evoked brain oscillations in mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 May 6;13(1):150. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02455-w. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37147311 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of NMDA-R antagonist, MK-801, on neuronal mismatch along the rat auditory thalamocortical pathway.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 24;10(1):12391. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68837-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32709861 Free PMC article.
-
Early auditory processing dysfunction in schizophrenia: Mechanisms and implications.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 May;148:105098. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105098. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 36796472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive visual evoked potentials under sevoflurane versus ketamine-xylazine in rats.Heliyon. 2021 Nov 9;7(11):e08360. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08360. eCollection 2021 Nov. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34816047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler, L. E. , Rose G., and Freedman R.. 1986. Neurophysiological studies of sensory gating in rats: effects of amphetamine, phencyclidine, and haloperidol. Biol. Psychiatry 21:787–798. - PubMed
-
- Baldeweg, T. , Spence S., Hirsch S. R., and Gruzelier J.. 1998. Gamma‐band electroencephalographic oscillations in a patient with somatic hallucinations. Lancet 352:620–621. - PubMed
-
- Beauchemin, M. B. L. 2005. Statistical analysis of the mismatch negativity: to a dilemma, an answer. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 1:18–24.
-
- Behrendt, R. P. 2003. Hallucinations: synchronisation of thalamocortical gamma oscillations underconstrained by sensory input. Conscious. Cogn. 12:413–451. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

