Enzymatic Cascade Reactions in Biosynthesis
- PMID: 30156048
- PMCID: PMC6529181
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201807844
Enzymatic Cascade Reactions in Biosynthesis
Abstract
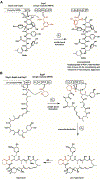
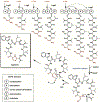
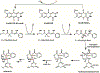
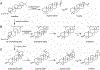
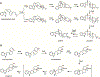
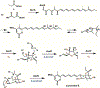
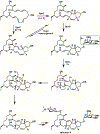
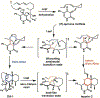
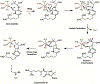
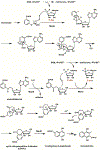
Enzyme-mediated cascade reactions are widespread in biosynthesis. To facilitate comparison with the mechanistic categorizations of cascade reactions by synthetic chemists and delineate the common underlying chemistry, we discuss four types of enzymatic cascade reactions: those involving nucleophilic, electrophilic, pericyclic, and radical reactions. Two subtypes of enzymes that generate radical cascades exist at opposite ends of the oxygen abundance spectrum. Iron-based enzymes use O2 to generate high valent iron-oxo species to homolyze unactivated C-H bonds in substrates to initiate skeletal rearrangements. At anaerobic end, enzymes reversibly cleave S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to generate the 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical as a powerful oxidant to initiate C-H bond homolysis in bound substrates. The latter enzymes are termed radical SAM enzymes. We categorize the former as "thwarted oxygenases".
Keywords: electrophilic cascades; natural products; nucleophilic cascades; pericyclic cascades; radical cascades.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures














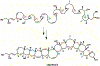

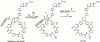














References
-
- Trost BM, Science 1991, 254, 1471–1477 - PubMed
- Trost BM, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 1995, 34, 259–281; Angew. Chem. 1995, 107, 285 – 307.
-
- Robinson R, J. Chem. Soc. Trans 1917, 111, 762–768
- Medley JW, Movassaghi M, Chem. Commun 2013, 49, 10775–10777. - PubMed
-
- Johnson WS, Gravestock MB, McCarry BE, J. Am. Chem. Soc 1971, 93, 4332–4334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

