Vasodilator-Stimulated Phosphoprotein: Regulators of Adipokines Resistin and Phenotype Conversion of Epicardial Adipocytes
- PMID: 30156215
- PMCID: PMC6126413
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.908111
Vasodilator-Stimulated Phosphoprotein: Regulators of Adipokines Resistin and Phenotype Conversion of Epicardial Adipocytes
Abstract
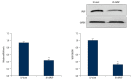
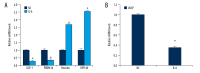
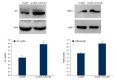
BACKGROUND Endothelial dysfunction plays a central part in the pathogenesis of coronary atherosclerosis. The adipokine resistin is one of the key players in endothelial cell dysfunction. In addition, the role of epicardial fat in coronary artery endothelial dysfunction is also emphasized. We investigated whether vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is involved in resistin-related endothelial dysfunction and the phenotype conversion of epicardial adipocytes. MATERIAL AND METHODS Cell proliferation and migration were evaluated by MTT and Transwell chamber assay, respectively. Next, we took epicardial fat samples from patients with valvular heart disease and non- coronary artery disease. Gene expression was determined by reverse transcription- quantitative polymerase chain reaction and relative abundance of the protein by Western blotting. RESULTS Resistin induced endothelial proliferation and migration in a dose-dependent manner. Both resistin-induced cell proliferation and migration were effectively blocked by ablation of VASP. The brown adipose tissue-specific genes for uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) and PR-domain-missing16 (PRDM16) decreased, but the white adipose tissue-specific genes for resistin and RIP140 increased in VASP-deficient adipocytes compared with the LV-sicntr group. However, disruption of the Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA) /Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) in VASP-deficient adipocytes with specific inhibitors inverted the adipocyte phenotype existing in VASP-deficient adipocytes. Furthermore, the expressions of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), and monocyte chemoattractantprotein-1 (MCP-1) in VASP-deficient adipocytes were markedly upregulated compared with the LV-sicntr group. CONCLUSIONS These results suggest a physiological role for VASP in coronary atherosclerosis through regulating adipokine resistin and phenotype conversion of epicardial adipose tissue.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A VASP-Rac-soluble guanylyl cyclase pathway controls cGMP production in adipocytes.Sci Signal. 2012 Aug 28;5(239):ra62. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002867. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22932701
-
CD40L/CD40 Regulates Adipokines and Cytokines by H3K4me3 Modification in Epicardial Adipocytes.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 1;78(2):228-234. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001060. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34029270
-
Increased expression and secretion of resistin in epicardial adipose tissue of patients with acute coronary syndrome.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):H746-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00617.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20061546
-
[Epicardial adipose tissue and its role in cardiac physiology and disease].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013 Jun 20;67:584-93. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1053908. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2013. PMID: 23799402 Review. Polish.
-
Human epicardial adipose tissue: a review.Am Heart J. 2007 Jun;153(6):907-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2007.03.019. Am Heart J. 2007. PMID: 17540190 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverging role of epicardial adipose tissue across the entire heart failure spectrum.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Dec;10(6):3419-3429. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14483. Epub 2023 Sep 11. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37697706 Free PMC article.
-
Adipogenesis: A Necessary but Harmful Strategy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 26;20(15):3657. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153657. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epicardial adipose tissue in contemporary cardiology.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022 Sep;19(9):593-606. doi: 10.1038/s41569-022-00679-9. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35296869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Significance of Detection of Peripheral Blood VASP Level in Lung Cancer Patients.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 31;2022:1703339. doi: 10.1155/2022/1703339. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9782723. doi: 10.1155/2023/9782723. PMID: 35958935 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Development of Atrial Fibrillation (AFIB) and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF).Cureus. 2023 Sep 28;15(9):e46153. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46153. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37900360 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM. Cardiovascular risk prediction: Basic concepts, current status, and future directions. Circulation. 2010;121:1768–77. - PubMed
-
- Kumar B, Chile SA, Ray KB, et al. VEGF-C differentially regulates VEGF-A expression in ocular and cancer cells; Promotes angiogenesis via RhoA mediated pathway. Angiogenesis. 2011;14:371–80. - PubMed
-
- Sacks HS, Fain JN, Bahouth SW, et al. Adult epicardial fat exhibits beige features. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:E1448–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

