Metabolic and Transcriptional Modules Independently Diversify Plasma Cell Lifespan and Function
- PMID: 30157439
- PMCID: PMC6172041
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.084
Metabolic and Transcriptional Modules Independently Diversify Plasma Cell Lifespan and Function
Abstract
Plasma cell survival and the consequent duration of immunity vary widely with infection or vaccination. Using fluorescent glucose analog uptake, we defined multiple developmentally independent mouse plasma cell populations with varying lifespans. Long-lived plasma cells imported more fluorescent glucose analog, expressed higher surface levels of the amino acid transporter CD98, and had more autophagosome mass than did short-lived cells. Low amino acid concentrations triggered reductions in both antibody secretion and mitochondrial respiration, especially by short-lived plasma cells. To explain these observations, we found that glutamine was used for both mitochondrial respiration and anaplerotic reactions, yielding glutamate and aspartate for antibody synthesis. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress responses, which link metabolism to transcriptional outcomes, were similar between long- and short-lived subsets. Accordingly, population and single-cell transcriptional comparisons across mouse and human plasma cell subsets revealed few consistent and conserved differences. Thus, plasma cell antibody secretion and lifespan are primarily defined by non-transcriptional metabolic traits.
Keywords: cell respiration; endoplasmic reticulum stress; glucose metabolism; glutamine metabolism; glycosylation; hexosamine biosynthesis; immunoglobulin biosynthesis; plasma cells; single-cell RNA-sequencing.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
D.B. is a co-founder of Cloak Therapeutics and owns significant equity. A patent application related to the current work has been filed (PCT/US18/23288). G.J.P. is a scientific advisory board member for Cambridge Isotope Laboratories. R.M.N. is a paid consultant for Biocomposites, Cardinal Health; CardioMEMS; DePuy, A Johnson & Johnson Company; Integra Sciences; Medtronic; Smith & Nephew; and Wright Medical Technology, Inc. W.Y.L. is an employee of Amgen Inc.
Figures
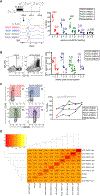

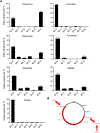
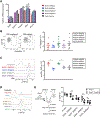


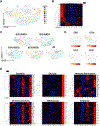
References
-
- Amanna IJ, Carlson NE, and Slifka MK (2007). Duration of humoral immunity to common viral and vaccine antigens. N. Engl. J. Med 357, 1903–1915. - PubMed
-
- An M, Ryu DR, Won Park J, Ha Choi J, Park EM, Eun Lee K, Woo M, and Kim M (2017). ULK1 prevents cardiac dysfunction in obesity through autophagy-meditated regulation of lipid metabolism. Cardiovasc. Res 113, 1137–1147. - PubMed
-
- Auner HW, Beham-Schmid C, Dillon N, and Sabbattini P (2010). The life span of short-lived plasma cells is partly determined by a block on activation of apoptotic caspases acting in combination with endoplasmic reticulum stress. Blood 116, 3445–3455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

