A case report of mucocutaneous tuberculosis after orthotopic liver transplantation: a challenging diagnosis
- PMID: 30157783
- PMCID: PMC6114782
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3347-7
A case report of mucocutaneous tuberculosis after orthotopic liver transplantation: a challenging diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Mycobacterium tuberculosis is responsible for high morbidity and mortality in immune-compromised hosts.
Case presentation: We present a rare case of cutaneous tuberculosis after orthotopic liver transplantation without involvement of any other organs.
Conclusion: TB risk-factors assessment, careful LTBI screening and treatment according to national guidelines, as well as a reduction in missed opportunity for prevention are necessary to avoid MTB related disease in fragile patients.
Keywords: Cutaneous tuberculosis; HCC; LTBI; OLT.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the patient (19 Dec 2017). A copy of the consent form is available for review by the Editor of this journal, it was submitted with the first version.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
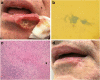
References
-
- Golden MP, Vikram HR. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis: an overview. Am Fam Physician. 2005;72(9):1761–1768. - PubMed
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2017, WHO. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/259366/1/9789241565516-eng.pdf?... (accessed on: 8 Feb 2018).
-
- Blasi F, Matteelli A, Sotgiu G, Cirillo DM, Palmieri F, Fattorini L, Migliori GB. Moving towards tuberculosis elimination: a call for action from Italy and a possible model for other low tuberculosis incidence countries. Eur Respir J. 2017;49(2). 10.1183/13993003.02242-2016. Print 2017 Feb. PubMed PMID: 28153873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

