The HSP90 Family: Structure, Regulation, Function, and Implications in Health and Disease
- PMID: 30158430
- PMCID: PMC6164434
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092560
The HSP90 Family: Structure, Regulation, Function, and Implications in Health and Disease
Abstract
The mammalian HSP90 family of proteins is a cluster of highly conserved molecules that are involved in myriad cellular processes. Their distribution in various cellular compartments underlines their essential roles in cellular homeostasis. HSP90 and its co-chaperones orchestrate crucial physiological processes such as cell survival, cell cycle control, hormone signaling, and apoptosis. Conversely, HSP90, and its secreted forms, contribute to the development and progress of serious pathologies, including cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, targeting HSP90 is an attractive strategy for the treatment of neoplasms and other diseases. This manuscript will review the general structure, regulation and function of HSP90 family and their potential role in pathophysiology.
Keywords: GRP94; HSP90; TRAP1; molecular chaperones; pathophysiology; structure and function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
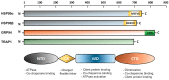
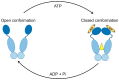
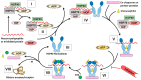
References
-
- Ritossa F. A new puffing pattern induced by temperature shock and DNP in drosophila. Experientia. 1962;18:571–573. doi: 10.1007/BF02172188. - DOI
-
- Malyshev I. Immunity, Tumors and Aging: The Role of HSP70. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2013. A General Description of HSPs, The Molecular Structure of HSP70 and The HSP70 Cycle; pp. 1–13.
-
- Pirkkala L., Sistonen L. Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs): Structure, Function and Genetics. Encycl. Life Sci. 2006:1–7. doi: 10.1038/npg.els.0006130. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

