Long-term outcome of mitomycin C-augmented needle revision of trabeculectomy blebs for late trabeculectomy failure
- PMID: 30158576
- PMCID: PMC6292892
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-018-0199-8
Long-term outcome of mitomycin C-augmented needle revision of trabeculectomy blebs for late trabeculectomy failure
Abstract
Objectives: To describe the 3-year outcomes of mitomycin C (MMC)-augmented bleb needling procedures following late trabeculectomy failure.
Methods: A retrospective, observational chart review of 44 eyes that underwent MMC-augmented bleb needling following late trabeculectomy failure. The primary outcome measure was IOP at 3 years post-operatively. Secondary outcome measures were the number of topical glaucoma medications and success rate at 3 years. Success was defined on the basis of IOP (≤21 mmHg and ≥5 mmHg with a reduction of ≥ 20% from pre-operative baseline), need for ocular hypotensive medications, and need for further laser or surgical intervention.
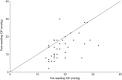
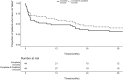
Results: Mean IOP was reduced from 19.8 mmHg preoperatively to 13.9 mmHg (29.5% reduction) at 3 years. By the 3-year time point, 26 eyes (59.1%) had met one or more of the criteria for failure. A lower immediate post-operative IOP was found to be associated with greater likelihood of success.
Conclusions: Bleb needling augmented with MMC can achieve a significant reduction in IOP in eyes with late trabeculectomy failure. By 3 years however, 59% of eyes were classified as failures, with half requiring further glaucoma surgery or laser. Patients undergoing this procedure should therefore be warned of the likelihood of requiring further intervention, and a repeat antimetabolite-augmented trabeculectomy or glaucoma tube shunt surgery in the first instance can be considered instead.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (2017). Glaucoma: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline (NG81). p. 13–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

