Melting conditions in the modern Tibetan crust since the Miocene
- PMID: 30158586
- PMCID: PMC6115434
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05934-7
Melting conditions in the modern Tibetan crust since the Miocene
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Melting conditions in the modern Tibetan crust since the Miocene.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 17;9(1):3831. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06344-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30224703 Free PMC article.
Abstract
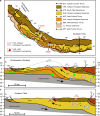
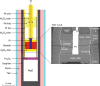
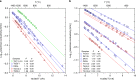
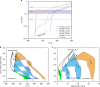
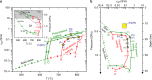
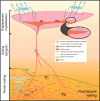
Abundant granitic rocks exposed in ancient mountain belts suggest that crustal melting plays a major role in orogenic processes. However, complex field relations and superposition of multiple tectonic events make it difficult to determine the role of melting in orogenesis. In contrast, geophysical measurements image present-day crustal conditions but cannot discriminate between partial melt and aqueous fluids. Here we connect pressure-temperature paths of Himalayan Miocene crustal rocks to the present-day conditions beneath the Tibetan plateau imaged with geophysical data. We use measurements of electrical conductivity to show that 4-16% water-rich melt is required to explain the crustal conductivity in the north-western Himalaya. In southern Tibet, higher melt fractions >30% reflect a crust that is either fluid-enriched (+1% H2O) or hotter (+100 °C) compared to the Miocene crust. These melt fractions are high enough for the partially molten rocks to be significantly weaker than the solid crust.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brown M. Granite: from genesis to emplacement. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2013;125:1079–1113. doi: 10.1130/B30877.1. - DOI
-
- Patiño Douce AE, Harris N. Experimental constraints on Himalayan anatexis. J. Petrol. 1998;39:689–710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689. - DOI
-
- Nábělek PI, Whittington AG, Hofmeister AM. Strain heating as a mechanism for partial melting and ultrahigh temperature metamorphism in convergent orogens: Implications of temperature-dependent thermal diffusivity and rheology. J. Geophys. Res. 2010;115:B12417. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007727. - DOI
-
- Searle M. Crustal melting, ductile flow, and deformation in mountain belts: cause and effect relationships. Lithosphere. 2013;5:547–554. doi: 10.1130/RF.L006.1. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 41372202/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 279790/EC | European Research Council (ERC)/International
- ANR-10-LABX-100-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)/International
- 41672197/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 279790/ERC_/European Research Council/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

