A general deoxygenation approach for synthesis of ketones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes
- PMID: 30158628
- PMCID: PMC6115474
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06019-1
A general deoxygenation approach for synthesis of ketones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes
Abstract
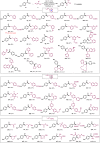
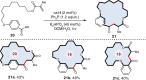
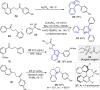
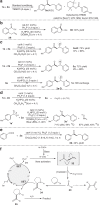
The construction of an aryl ketone structural unit by means of catalytic carbon-carbon coupling reactions represents the state-of-the-art in organic chemistry. Herein we achieved the direct deoxygenative ketone synthesis in aqueous solution from readily available aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes, affording structurally diverse ketones in moderate to good yields. Visible-light photoredox catalysis enables the direct deoxygenation of acids as acyl sources with triphenylphosphine and represents a distinct perspective on activation. The synthetic robustness is supported by the late-stage modification of several pharmaceutical compounds and complex molecules. This ketone synthetic strategy is further applied to the synthesis of the drug zolpidem in three steps with 50% total yield and a concise construction of cyclophane-braced 18-20 membered macrocycloketones. It represents not only the advancement for the streamlined synthesis of aromatic ketones from feedstock chemicals, but also a photoredox radical activation mode beyond the redox potential of carboxylic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Gooßen Lukas J, et al. New catalytic transformations of carboxylic acids. Pure Appl. Chem. 2008;80:1725–1733. doi: 10.1351/pac200880081725. - DOI
-
- Pedley, J. B. Thermochemical Data and Structure of Organic Compounds, (Texas A & M Univ., Texas, 1994).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

