Triplet Excited Carbonyls and Singlet Oxygen Formation During Oxidative Radical Reaction in Skin
- PMID: 30158877
- PMCID: PMC6104306
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01109
Triplet Excited Carbonyls and Singlet Oxygen Formation During Oxidative Radical Reaction in Skin
Abstract
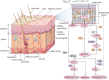
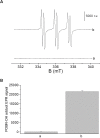
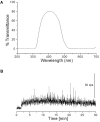
The skin is the largest organ in the body and is consistently exposed to aggressive environmental attacks (biological/physical/chemical, etc.). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are formed during the normal oxidative metabolism which enhances to a lethal level under stress conditions referred to as oxidative stress. While, under normal conditions, cells are capable of dealing with ROS using non-enzymatic and enzymatic defense system, it can lead to a critical damage to cell system via the oxidation of cellular components under stress condition. Lipid peroxidation is a well-established mechanism of cellular injury in all kinds of organisms and it is often used as an indicator of oxidative stress in cells and tissues. In the presence of metal ions, ROS such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produces highly reactive hydroxyl radical (HO•) via Fenton reaction. In the current study, we have used the porcine skin (intact pig ear/skin biopsies) as an ex vivo/in vitro model system to represent human skin. Experimental results have been presented on the participation of HO• in the initiation of lipid peroxidation and thereby leading to the formation of reactive intermediates and the formation of electronically excited species eventually leading to ultra-weak photon emission (UPE). To understand the participation of different electronically excited species in the overall UPE, the effect of a scavenger of singlet oxygen (1O2) on photon emission in the visible and near-infrared region of the spectrum was measured which showed its contribution. In addition, measurement with interference filter with a transmission in the range of 340-540 nm reflected a substantial contribution of triplet carbonyls (3L=O∗) in the photon emission. Thus, it is concluded that during the oxidative radical reactions, the UPE is contributed by the formation of both 3L=O∗ and 1O2. The method used in the current study is claimed to be a potential tool for non-invasive determination of the physiological and pathological state of human skin in dermatological research.
Keywords: singlet oxygen; skin; triplet excited carbonyl; two-dimensional photon imaging; ultra-weak photon emission.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of reactive oxygen species in ultra-weak photon emission in biological systems.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014 Oct 5;139:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.02.008. Epub 2014 Mar 3. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014. PMID: 24674863 Review.
-
Imaging and Characterization of Oxidative Protein Modifications in Skin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3981. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043981. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835390 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the Formation of Electronically Excited Species by Oxidative Metabolic Processes: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 5;9(7):258. doi: 10.3390/biom9070258. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31284470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Free oxygen radiacals and kidney diseases--part I].Med Pregl. 2000 Sep-Oct;53(9-10):463-74. Med Pregl. 2000. PMID: 11320727 Review. Croatian.
-
Linoleic acid-induced ultra-weak photon emission from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as a tool for monitoring of lipid peroxidation in the cell membranes.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022345. Epub 2011 Jul 25. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799835 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Priming as a Tool in Redox and Mitochondrial Theragnostics.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 10;12(5):1072. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051072. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time monitoring of cellular superoxide anion release in THP-1 cells using a catalytically amplified superoxide dismutase-based microbiosensor.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Sep;416(21):4727-4737. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05437-z. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39014219
-
Ultra weak photon emission-a brief review.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 14;15:1348915. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1348915. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38420619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and purification of Eleutherococcus sessiliflorus (Rupr. & Maxim.) S. Y. Hu peptides and study of their antioxidant effects and mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 8;15:1353871. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1353871. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38389921 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiolipin Structure and Oxidation Are Affected by Ca2+ at the Interface of Lipid Bilayers.Front Chem. 2020 Jan 21;7:930. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00930. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32039150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam W., Cilento G. (1982). Chemical and Biological Generation of Excited States. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press.
-
- Avon S. L., Wood R. E. (2005). Porcine skin as an in-vivo model for ageing of human bite marks. J. For. Odonto Stomatol. 23 30–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

