Serum Apelin and Obesity-Related Complications in Egyptian Children
- PMID: 30159056
- PMCID: PMC6108807
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.312
Serum Apelin and Obesity-Related Complications in Egyptian Children
Abstract
Background: The rapidly increasing prevalence of childhood obesity became a major burden on health worldwide, giving an alarm to clinicians and researchers. Adipocytes act as an active endocrine organ by releasing plenty of bioactive mediators (adipokines) that play a major role in regulating metabolic processes. Apelin is a recently identified adipokine that is expressed in adipocytes.
Aim: The current work aimed to uncover the relation between serum apelin and childhood obesity and its related complications as hypertension and hyperglycemia.
Method: A group of 50 obese and 31 non-obese; sex- and age-matched children were enrolled in our study with a mean age of (9.5 ± 2.1) and (8.7 ± 1.3) respectively. Anthropometric measurements, blood pressure, were assessed in all studied participants, we also determined the lipid profile, serum insulin, fasting blood glucose (FBG) level, HOMA-IR and serum apelin.
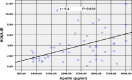
Results: Obese children had higher levels of HbA1c, FBG, serum insulin, HOMA-IR, total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP Z-score); compared to controls (all P < 0.05). Apelin was significantly higher in obese children versus controls and correlated positively with BMI Z-Score (P = 0.008), DBP Z-Score (P = 0.02), cholesterol, TG (both P = 0.02), serum insulin (P = 0.003), FBG and HOMA-IR (both P = 0.001). Linear regression analysis showed that FBG was the most effective factor in predicting the level of serum apelin (P = 0.04).
Conclusion: This work supports the hypothesis that apelin may have a crucial role in the pathogenesis of health hazards related to obesity in children including insulin resistance, hypertension and a higher risk of occurrence of metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Apelin; Children; Metabolic syndrome; Obesity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum apelin-12 and obesity-related markers in Egyptian children with Down syndrome.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Jan;183(1):461-470. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05315-3. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37930396 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between serum apelin-12 levels and obesity-related markers in Chinese children.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e86577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086577. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475149 Free PMC article.
-
Serum apelin levels and metabolic risk markers in obese women.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2017 Dec;15(2):423-429. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 Jun 9. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 30647682 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Apelin Levels in Overweight-obese Children with Pubertal Development, but Not with Insulin Sensitivity: 6.5 Years Follow up Evaluation.Endocr Res. 2020 Nov;45(4):233-240. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2020.1804929. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Endocr Res. 2020. PMID: 32791927
-
Associations Between Thyroid Hormones Within the Euthyroid Range and Indices of Obesity in Obese Chinese Women of Reproductive Age.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019 Oct;17(8):416-422. doi: 10.1089/met.2019.0036. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 31355704
Cited by
-
The Effect of a Multidisciplinary Lifestyle Intervention Program on Apelin-12, Vaspin and Resistin Concentrations in Children and Adolescents with Overweight and Obesity.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 26;16(21):3646. doi: 10.3390/nu16213646. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519480 Free PMC article.
-
Alarming Eating Behaviours among Adolescents in Egypt.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Jul 13;7(13):2189-2193. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.583. eCollection 2019 Jul 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31456850 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin-13 and Asprosin in Adolescents with Anorexia Nervosa and Their Association with Psychometric and Metabolic Variables.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 28;14(19):4022. doi: 10.3390/nu14194022. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235674 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of serum apelin level with carotid intima-media thickness and insulin resistance in a sample of Egyptian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Res Med Sci. 2022 Feb 18;27:13. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_675_20. eCollection 2022. J Res Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342448 Free PMC article.
-
Adipokines, Myokines, and Cardiokines: The Role of Nutritional Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 8;21(21):8372. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218372. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33171610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caprio S. Insulin resistance in childhood obesity. Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism: JPEM. 2002;15:487–92. PMid:12017221. - PubMed
-
- Kwiterovich PO., Jr Recognition and management of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2008;93:4200–4209. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-1270 PMid:18697860. - PubMed
-
- Weiss R, Kaufman FR. Metabolic complications of childhood obesity: identifying and mitigating the risk. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 2):310–316. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-s273 PMid:18227502. - PubMed
-
- Arslanian S. Type 2 diabetes in children: clinical aspects and risk factors. Hormone Research. 2002;(Suppl 1):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1159/000053308. - PubMed
-
- Mattsson N, Ro¨nnemaa T, Juonala M, Viikari JS, Raitakari OT. Childhood predictors of the metabolic syndrome in adulthood. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Annals of Medicine. 2008;40(7):254–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890802307709 PMid:18728920. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous