Sac-Type Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report of Two Siblings
- PMID: 30159188
- PMCID: PMC6109563
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/3270526
Sac-Type Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report of Two Siblings
Abstract
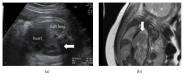
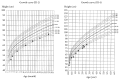
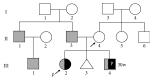
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH), a herniation of the abdominal contents through a defect or hypoplasia of the diaphragm, is a relatively common, severe congenital anomaly. Here we present the first case of two siblings with possibly isolated sac-type CDH and with a suspected genetic etiology. Although sibling recurrence of isolated CDH is rare, the incidence is higher than in the general population. Additionally, the second child had a more severe respiratory disorder than the first child. It is to be noted that siblings of children having isolated CDH are at risk for CDH, and prenatal evaluation should be considered individually.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Familial severe congenital diaphragmatic hernia: left herniation in one sibling and bilateral herniation in another.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2013 Mar;53(1):54-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-4520.2012.00363.x. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2013. PMID: 23480359
-
Late-presenting congenital diaphragmatic hernia in children: a clinical spectrum.Pediatr Surg Int. 2004 Sep;20(9):658-69. doi: 10.1007/s00383-004-1269-5. Epub 2004 Sep 3. Pediatr Surg Int. 2004. PMID: 15349741 Review.
-
Two cases of right congenital diaphragmatic hernia with stable respiratory condition: Two case reports.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Jan;114:109036. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.109036. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38039568 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal ultrasonography for evaluation of hernia sac of neonate with congenital diaphragmatic hernia.Radiol Case Rep. 2019 Mar 26;14(6):683-686. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2019.03.012. eCollection 2019 Jun. Radiol Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30976368 Free PMC article.
-
The etiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: still largely unknown?Eur J Med Genet. 2009 Sep-Oct;52(5):281-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 May 21. Eur J Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 19464395 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

