Effects of vitamin D optimization on quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30159280
- PMCID: PMC6108287
- DOI: 10.14196/mjiri.32.29
Effects of vitamin D optimization on quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
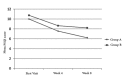
Background: Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the frequency of hypovitaminosis D in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) and its association with FMS symptoms. This study aimed at assessing the effect of hypovitaminosis D on the symptoms and quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia. Methods: A total of 74 FMS patients with hypovitaminosis D were randomly assigned into group A (Trazodone 25 mg at bedtime + vitamin D 50 000 IU weekly) and group B (Trazodone 25 mg at bedtime + placebo). Serum vitamin D level, Widespread Pain Index (WPI), Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) were used at the beginning of the treatment and 4 and 8 weeks post treatment. Results: Significant improvements were observed in WPI, FIQ, and PSQI scores in both groups. Moreover, combination of vitamin D and Trazodone resulted in significant improvement of SF-36 scores compared to Trazodone therapy. Improvement in pain-related indices including the WPI and the physical component score (PCS) fraction of SF-36 was more noticeable in vitamin D/Trazodone combination therapy. Conclusion: This study suggests that vitamin D supplementation has significant therapeutic benefits in the management of FMS, especially in pain reduction of patients with fibromyalgia. According to our results, a combination of vitamin D supplements and a conventional antidepressant, when given to vitamin D-deficient fibromyalgia patients, could significantly improve both physical and psychological symptoms.
Keywords: Fibromyalgia syndrome; Pain; Quality of life; Vitamin D.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of rehabilitation with Tai Ji Quan in an Italian cohort of patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2016 Aug;24:109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 27. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 27502810 Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of fibromyalgia on health status according to the types, demographic background and pain index.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Mar-Apr;34(2 Suppl 96):S134-9. Epub 2016 May 2. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27157398
-
Fibromyalgia syndrome: is it related to vitamin D deficiency in premenopausal female patients?Pain Manag Nurs. 2013 Dec;14(4):e156-e163. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2011.09.006. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Pain Manag Nurs. 2013. PMID: 24315268
-
Psychological Outcomes and Quality of Life of Fibromyalgia Patients with Vitamin D Supplementation-A Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 6;12(7):2750. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072750. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Vitamin D Supplementation in the Improvement of Clinical Status in Patients Diagnosed with Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Systematic Review.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2022;18(4):317-328. doi: 10.2174/1573397118666220307122152. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35255799
Cited by
-
Association of Serum Vitamin D with Serum Cytokine Profile in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(1_suppl):1610S-1618S. doi: 10.1177/19476035211010309. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 33890506 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Vitamin D Supplementation in the Treatment of Fibromyalgia Syndrome and Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain.Nutrients. 2022 Jul 22;14(15):3010. doi: 10.3390/nu14153010. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35893864 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of vitamin D treatment on quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Apr;193(2):1111-1116. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03521-4. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37707690 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of weekly vitamin D3 in patients with fibromyalgia: 12-week, double-blind, randomized, controlled placebo trial.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;40(8):3257-3264. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05640-8. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33570701 Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Vitamin D in the Management of Chronic Pain in Fibromyalgia: A Narrative Review.Health Psychol Res. 2021 Jun 28;9(1):25208. doi: 10.52965/001c.25208. eCollection 2021. Health Psychol Res. 2021. PMID: 35106398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolfe F. Fibromyalgia. Prognosis in the Rheumatic Diseases: Springer; 1991. p. 321-32.
-
- Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, Russell IJ, Hebert L. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(1):19–28. - PubMed
-
- Burckhardt CS, Clark S, Bennett RR. Fibromyalgia and quality of life. J Rheumtol. 1993;20(3):475–9. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong D, Meenagh G, Bickle I, Lee A, Curran E-S, Finch M. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with anxiety and depression in fibromyalgia. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26(4):551–4. - PubMed
-
- Wepner F, Scheuer R, Schuetz-Wieser B, Machacek P, Pieler-Bruha E, Cross HS. et al. Effects of vitamin D on patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. PAIN. 2014;155(2):261–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous