Analysis of Epistasis in Natural Traits Using Model Organisms
- PMID: 30166071
- PMCID: PMC6541385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.08.002
Analysis of Epistasis in Natural Traits Using Model Organisms
Abstract
The ability to detect and understand epistasis in natural populations is important for understanding how biological traits are influenced by genetic variation. However, identification and characterization of epistasis in natural populations remains difficult due to statistical issues that arise as a result of multiple comparisons, and the fact that most genetic variants segregate at low allele frequencies. In this review, we discuss how model organisms may be used to manipulate genotypic combinations to power the detection of epistasis as well as test interactions between specific genes. Findings from a number of species indicate that statistical epistasis is pervasive between natural genetic variants. However, the properties of experimental systems that enable analysis of epistasis also constrain extrapolation of these results back into natural populations.
Keywords: allele frequency; epistasis; mechanism of epistasis; natural genetic variation.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
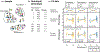
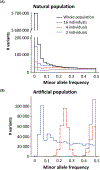
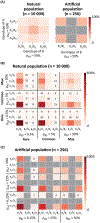
References
-
- Cordell HJ (2002) Epistasis: what it means, what it doesn't mean, and statistical methods to detect it in humans. Hum Mol Genet 11 (20), 2463–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

