A study paradigm integrating prospective epidemiologic cohorts and electronic health records to identify disease biomarkers
- PMID: 30166544
- PMCID: PMC6117367
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05624-4
A study paradigm integrating prospective epidemiologic cohorts and electronic health records to identify disease biomarkers
Abstract
Defining the full spectrum of human disease associated with a biomarker is necessary to advance the biomarker into clinical practice. We hypothesize that associating biomarker measurements with electronic health record (EHR) populations based on shared genetic architectures would establish the clinical epidemiology of the biomarker. We use Bayesian sparse linear mixed modeling to calculate SNP weightings for 53 biomarkers from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. We use the SNP weightings to computed predicted biomarker values in an EHR population and test associations with 1139 diagnoses. Here we report 116 associations meeting a Bonferroni level of significance. A false discovery rate (FDR)-based significance threshold reveals more known and undescribed associations across a broad range of biomarkers, including biometric measures, plasma proteins and metabolites, functional assays, and behaviors. We confirm an inverse association between LDL-cholesterol level and septicemia risk in an independent epidemiological cohort. This approach efficiently discovers biomarker-disease associations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
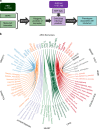
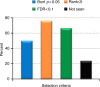
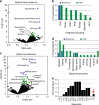

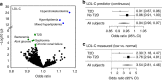
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006389/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 15MCPRP25620006/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)/International
- U01 HG006830/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006375/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM120523/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008657/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006382/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010685/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 16FTF30130005/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006380/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133786/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074711/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000446/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006388/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008685/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

