PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: THE INTERSECTION OF GENETICS AND EPIGENETICS
- PMID: 30166712
- PMCID: PMC6116585
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: THE INTERSECTION OF GENETICS AND EPIGENETICS
Abstract
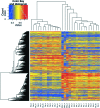
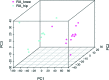
Rheumatoid arthritis is a synovial inflammatory disease marked by joint infiltration by immune cells and damage to the extracellular matrix. Although genetics plays a critical role in heritability and its pathogenesis, the relative lack of disease concordance in identical twins suggests that noncoding influences can affect risk and severity. Environmental stress, which can be reflected in the genome as altered epigenetic marks, also contributes to gene regulation and contributes to disease mechanisms. Studies on DNA methylation suggest that synovial cells, most notably fibroblast-like synoviocytes, are imprinted in rheumatoid arthritis with epigenetic marks and subsequently assume an aggressive phenotype. Even more interesting, the synoviocyte marks are not only disease specific but can vary depending on the joint of origin. Understanding the epigenetic landscape using unbiased methods can potentially identify nonobvious pathways and genes that that are responsible for synovial inflammation as well as the diversity of responses to targeted agents. The information can also be leveraged to identify novel therapeutic approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest: This work was funded in part by grants from the Rheum-atology Research Foundation, the Arthritis Foundation, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (R01 AR065466). Dr. Firestein has received grant funding from Gilead Sciences and Janssen Pharmaceuticals; and he has received consulting income from Roche and Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic alterations in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Epigenomics. 2017 Apr;9(4):479-492. doi: 10.2217/epi-2016-0151. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Epigenomics. 2017. PMID: 28322585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics, epigenetics and autoimmunity constitute a Bermuda triangle for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Life Sci. 2024 Nov 15;357:123075. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123075. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39341491 Review.
-
The Mechanisms Underlying Chronic Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis from the Perspective of the Epigenetic Landscape.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:6290682. doi: 10.1155/2016/6290682. Epub 2016 Dec 28. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 28116320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint-specific DNA methylation and transcriptome signatures in rheumatoid arthritis identify distinct pathogenic processes.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 10;7:11849. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11849. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27282753 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive epigenetic landscape of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Nat Commun. 2018 May 15;9(1):1921. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04310-9. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29765031 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Frequency and Predictors of Opioid Use in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy Patients.Addict Health. 2022 Oct;14(4):250-255. doi: 10.34172/ahj.2022.1332. Epub 2022 Oct 29. Addict Health. 2022. PMID: 37559793 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of the Vitamin D Receptor Gene in Human Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 20;25(1):107. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010107. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Epigenetic Changes in Vitamin D Pathway Genes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Acta Med Litu. 2022;29(1):78-90. doi: 10.15388/Amed.2021.29.1.7. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Acta Med Litu. 2022. PMID: 36061943 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Efficacy of Influenza Vaccination in Autoimmune Disease Patients.Cureus. 2021 May 13;13(5):e15016. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15016. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34136315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential mechanisms of action of celastrol against rheumatoid arthritis: Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 29;15(7):e0233814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233814. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32726313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Kelley and Firestein’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Elsevier; Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 2016 1115–66.
-
- Hill JA, Southwood S, Sette A, Jevnikar AM, Bell DA, et al. Cutting edge: the conversion of arginine to citrulline allows for a high-affinity peptide interaction with the rheumatoid arthritis-associated HLA-DRB1*0401 MHC class II molecule. J Immunol. 2003;171:538–41. - PubMed
-
- Aho K, Koskenvuo M, Tuominen J, Kaprio J. Occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis in a nationwide series of twins. J Rheumatol. 1986;13:899–902. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
