An Evolving Approach to the Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- PMID: 30166949
- PMCID: PMC6111507
An Evolving Approach to the Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
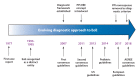
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic allergic/ immune-mediated esophageal disease. Knowledge related to the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, epidemiology, natural history, treatment, and outcomes of EoE has rapidly evolved over the past 2 decades. This article focuses on the similarly evolving diagnostic framework for EoE. In the initial clinical guidelines, diagnosis of EoE was based on symptoms of esophageal dysfunction; at least 15 eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf) on esophageal biopsy; and either a lack of response to high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy, or normal pH monitoring. The first 2 criteria have remained largely unchanged; however, the role of PPIs has been controversial, particularly due to the recognition of PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE), in which patients with suspected EoE experience resolution of symptoms and esophageal eosinophilia with PPI therapy. A quickly expanding evidence base has found that most adult patients with EoE and PPI-REE share similar clinical, endoscopic, histologic, immunologic, and molecular characteristics prior to the use of PPIs. Because of this, the most recent diagnostic guidelines have removed the lack of response to PPIs as a diagnostic criterion; PPIs are now better considered as a treatment for esophageal eosinophilia. EoE should currently be suspected on a clinical basis when there are symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and at least 15 eos/hpf on esophageal biopsies. A history of atopy and endoscopic signs of EoE are strongly supportive of the diagnosis. However, the diagnosis cannot be confirmed until a thorough evaluation of other potential causes of esophageal eosinophilia has been performed.
Keywords: Eosinophilic esophagitis; diagnosis; eosinophil; esophageal eosinophilia; esophagus.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by NIH Awards T32 DK007634 (HPK) and R01 DK101856 (ESD). Dr Dellon is a consultant for Adare Pharmaceuticals, Alivio Therapeutics, Allakos, AstraZeneca, Banner Health, Enumeral Biomedical, GlaxoSmithKline, Receptos/Celgene, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Robarts Clinical Trials, and Shire. He receives research funding from Adare Pharmaceuticals, Meritage Pharma, Miraca Life Sciences, Nutricia, Receptos/Celgene, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Shire, and has received an educational grant from Banner Health and Holoclara. Dr Kim has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128(1):3–20.e6. - PubMed
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA. American College of Gastroenterology. ACG Clinical Guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(5):679–692. - PubMed
-
- Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6):1230–1236.e1-e2. - PubMed
-
- Lipka S, Keshishian J, Kumar A, Richter J. Time-dependent association of untreated eosinophilic esophagitis and the risk of esophageal stricture in a U.S. population. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(5):S669–S670.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
