Can power Doppler ultrasound of the entheses help in classifying recent axial spondyloarthritis? Data from the DESIR cohort
- PMID: 30167327
- PMCID: PMC6112385
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000686
Can power Doppler ultrasound of the entheses help in classifying recent axial spondyloarthritis? Data from the DESIR cohort
Abstract
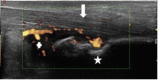
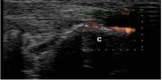
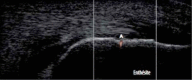
Early diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) remains a challenge due to the lack of specificity of clinical symptoms and variable prevalence of axial imaging findings permitting a definite diagnosis. Power Doppler ultrasonography (PDUS) of the entheses has demonstrated to be a potential useful tool for the classification and diagnostic management of early SpA independently of the phenotype.
Objectives: To assess the classification value (sensitivity and specificity) of PDUS-defined enthesitis for identifying patients fulfilling Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) classification criteria for axSpA (ASAS+) in patients with recent inflammatory back pain (IBP) (the DESIR (DEvenir des Spondylarthropathies Indifférenciées Récentes) cohort).
Methods: Baseline PDUS was performed at eight entheseal sites, and PDUS enthesitis was defined by the presence of vascularisation at entheseal insertion.
Results: 402 patients from the DESIR cohort underwent a PDUS evaluation. PDUS enthesitis was detected in 58 (14.4%) patients of whom 40 (14.2%) belonged to the ASAS+ patients and 18 (17%) to the ASAS- patients. The sensitivity of PDUS enthesitis was 13.9% and the specificity was 83.5%, with a positive predictive value of 69% and 26.8% of negative predictive value for meeting ASAS criteria for axSpA. Of the 18 ASAS- patients with positive PDUS, 59% fulfilled Amor's criteria, 88% European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group criteria and 59% both.
Conclusions: In a cohort of patients with recent IBP, the prevalence of PDUS enthesitis was low (14.4%); however, its specificity for classifying patients as axSpA according to ASAS criteria was high (83.5%). PDUS enthesitis might be of additional value for classifying as patients with axSpA IBP who do not fulfil ASAS criteria.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; enthesitis; spondyloarthritis; tendinitis; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PC has received consulting fees, speaking fees and/or honoraria from Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche-Chugai, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Janssen, Novartis, Celgene and UCB (less than US$10 000 each) and has been an investigator for Roche-Chugai, Sanofi Aventis, Abbvie, Pfizer, Celgene, UCB and BMS. MAD’A has received consulting fees and or speaking fees (less than US$10 000 each) from BMS, Roche-Chugai, Abbvie, MSD, Novartis and Pfizer and she is the PI of an academic multicentre clinical study which received a grant from Pfizer. MD has received consulting fees and or speaking fees (less than US$10 000 each) from BMS, Roche-Chugai, Abbvie, MSD, Novartis and Pfizer and he is the PI of an academic multicentre clinical study which received a grant from Pfizer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What is axial spondyloarthritis? A latent class and transition analysis in the SPACE and DESIR cohorts.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Mar;79(3):324-331. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216516. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31980546
-
Is a positive family history of spondyloarthritis relevant for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis once HLA-B27 status is known?Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Sep 1;58(9):1649-1654. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez095. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30938446 Free PMC article.
-
Is the current ASAS expert definition of a positive family history useful in identifying axial spondyloarthritis? Results from the SPACE and DESIR cohorts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 May 31;19(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1335-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28569222 Free PMC article.
-
Optimisation of rheumatology assessments - the actual situation in axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014 Sep-Oct;32(5 Suppl 85):S-96-104. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25365096 Review.
-
Classification and diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis--what is the clinically relevant difference?J Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;42(1):31-8. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.130959. Epub 2014 Nov 15. J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25399389 Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral enthesitis assessed by whole-body MRI in axial spondyloarthritis: Distribution and diagnostic value.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 23;13:976800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.976800. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36081521 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Review of the Classification and Use of Diagnostic Ultrasound for Conditions of the Achilles Tendon.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Nov 13;10(11):944. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110944. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33202763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Inclusion of Non-Inflammatory Ultrasonographic Enthesopathy Findings in Enthesitis Scoring Indices.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 8;11(4):669. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11040669. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving Imaging Modalities in Early Psoriatic Arthritis: The Role of Ultrasound in Early Diagnosis of Psoriatic Arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 7;8:804695. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.804695. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35071281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rudwaleit M, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, et al. . The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:770–6. 10.1136/ard.2009.108217 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moltó A, Paternotte S, Comet D, et al. . Performances of the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society axial spondyloarthritis criteria for diagnostic and classification purposes in patients visiting a rheumatologist because of chronic back pain: results from a multicenter, cross-sectional study. Arthritis Care Res 2013;65:1472–81. 10.1002/acr.22016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheung PP, Paternotte S, Burki V, et al. . Performance of the assessment in Spondyloarthritis International Society classification for axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis in an established clinical cohort: comparison with criteria sets of Amor and the European Spondylarthropathy Study Group. J Rheumatol 2012;39:816–21. 10.3899/jrheum.111088 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
