The potential of agricultural land management to contribute to lower global surface temperatures
- PMID: 30167456
- PMCID: PMC6114992
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaq0932
The potential of agricultural land management to contribute to lower global surface temperatures
Abstract
Removal of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) combined with emission reduction is necessary to keep climate warming below the internationally agreed upon 2°C target. Soil organic carbon sequestration through agricultural management has been proposed as a means to lower atmospheric CO2 concentration, but the magnitude needed to meaningfully lower temperature is unknown. We show that sequestration of 0.68 Pg C year-1 for 85 years could lower global temperature by 0.1°C in 2100 when combined with a low emission trajectory [Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) 2.6]. This value is potentially achievable using existing agricultural management approaches, without decreasing land area for food production. Existing agricultural mitigation approaches could lower global temperature by up to 0.26°C under RCP 2.6 or as much as 25% of remaining warming to 2°C. This declines to 0.14°C under RCP 8.5. Results were sensitive to assumptions regarding the duration of carbon sequestration rates, which is poorly constrained by data. Results provide a framework for the potential role of agricultural soil organic carbon sequestration in climate change mitigation.
Figures
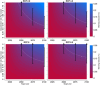
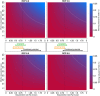
References
-
- Fuss S., Canadell J. G., Peters G. P., Tavoni M., Andrew R. M., Ciais P., Jackson R. B., Jones C. D., Kraxner F., Nakicenovic N., Quéré C. L., Raupach M. R., Sharifi A., Smith P., Yamagata Y., Betting on negative emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 4, 850–853 (2014).
-
- L. Clarke, K. Jiang, K. Akimoto, M. Babiker, G. Blanford, K. Fisher-Vanden, J. C. Hourcade, V. Krey, E. Kriegler, S. Loeschel, Assessing transformation pathways, in Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change, Working Group III Contribution to the IPCC 5th Assessment Report, O. Edenhofer, R. Pichs-Madruga, Y. Sokona, J. C. Minx, E. Farahani, S. Kadner, K. Seyboth, A. Adler, I. Baum, S. Bruner, P. Eickemeier, B. Kriemann, J. Savolainen, S. Schlömer, C. von Stechow, T. Zwickel, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2014).
-
- Bai Z. G., Dent D. L., Olsson L., Schaepman M. E., Proxy global assessment of land degradation. Soil Use Manag. 24, 223–234 (2008).
-
- Paustian K., Andrén O., Janzen H. H., Lal R., SMith P., Tian G., Tiessen H., Van Noordwijk M., Woomer P. L., Agricultural soils as a sink to mitigate CO2 emissions. Soil Use Manag. 13, 230–244 (1997).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

