Synthesis and characterization of Zinc/Chitosan-Folic acid complex
- PMID: 30167495
- PMCID: PMC6113674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00737
Synthesis and characterization of Zinc/Chitosan-Folic acid complex
Abstract
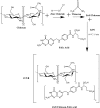
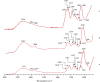
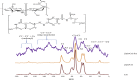
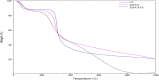
Therapeutic drug delivery systems using polymeric materials is an emerging field of research. However, the use of certain polymers has gained much-needed attention by the researchers due to their low toxic nature. In recent years, chitosan has gained popularity as a potential biodegradable polymer that can be used as a component in drug delivery systems. In this study, we synthesized a chitosan derivative that is composed of both folic acid and zinc and may serve as a viable component of a drug delivery system. The results of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), solid-state 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) and UV-visible Spectroscopy demonstrated a substantial difference between chitosan and ZnS/Chitosan-Folic acid derivative. The results were also confirmed using Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) techniques. The average particle size of the ZnS/Chitosan-Folic acid system was measured to be 463.67 ± 5.76 nm, showing that the product is within the nano-size range.
Keywords: Materials science.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Adilee K.J., Abass A.K., Taher A.M. Synthesis of some transition metal complexes with new heterocyclic thiazolyl azo dye and their uses as sensitizers in photo reactions. J. Mol. Struct. 2016;1108:378–397.
-
- Bakrudeen H.B., Sugunalakshmi M., Reddy B.S.R. Auto-fluorescent mesoporous ZnO nanospheres for drug delivery Carrier application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015;56:335–340. - PubMed
-
- Bujňáková Z., Dutková E., Zorkovská A., Baláž M., Kováč J., Kello M., Mojžiš J., Briančin J., Baláž P. Mechanochemical synthesis and in vitro studies of chitosan-coated InAs/ZnS mixed nanocrystals. J. Mater. Sci. 2017;52(2):721–735.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

