T cell receptor sequencing of activated CD8 T cells in the blood identifies tumor-infiltrating clones that expand after PD-1 therapy and radiation in a melanoma patient
- PMID: 30167863
- PMCID: PMC6196100
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-018-2228-7
T cell receptor sequencing of activated CD8 T cells in the blood identifies tumor-infiltrating clones that expand after PD-1 therapy and radiation in a melanoma patient
Abstract
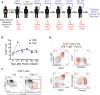
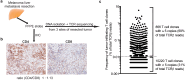
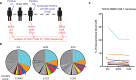
PD-1-targeted therapy has dramatically changed advanced cancer treatment. However, many questions remain, including specificity of T cells activated by PD-1 therapy and how peripheral blood analysis correlates to effects at tumor sites. In this study, we utilized TCR sequencing to dissect the composition of peripheral blood CD8 T cells activated upon therapy, comparing it with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. We report on a nonagenarian melanoma patient who showed a prominent increase in peripheral blood Ki-67 + CD8 T cells following brain stereotactic radiation and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Proliferating CD8 T cells exhibited an effector-like phenotype with expression of CD38, HLA-DR and Granzyme B, as well as expression of the positive costimulatory molecules CD28 and CD27. TCR sequencing of peripheral blood CD8 T cells revealed a highly oligoclonal repertoire at baseline with one clonotype accounting for 30%. However, the majority of dominant clones-including a previously identified cytomegalovirus-reactive clone-did not expand following treatment. In contrast, expanding clones were present at low frequencies in the peripheral blood but were enriched in a previously resected liver metastasis. The patient has so far remained recurrence-free for 36 months, and several CD8 T cell clones that expanded after treatment were maintained at elevated levels for at least 8 months. Our data show that even in a nonagenarian individual with oligoclonal expansion of CD8 T cells, we can identify activation of tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cell clones in peripheral blood following anti-PD-1-based immunotherapies.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; Immunotherapy; Melanoma; PD-1; T cell repertoire.
Conflict of interest statement
Rafi Ahmed is an inventor on patents held by Emory University that cover the topic of PD-1-directed immunotherapy. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, Gogas HJ, Arance AM, Cowey CL, Dalle S, Schenker M, Chiarion-Sileni V, Marquez-Rodas I, Grob JJ, Butler MO, Middleton MR, Maio M, Atkinson V, Queirolo P, Gonzalez R, Kudchadkar RR, Smylie M, Meyer N, Mortier L, Atkins MB, Long GV, Bhatia S, Lebbe C, Rutkowski P, Yokota K, Yamazaki N, Kim TM, de Pril V, Sabater J, Qureshi A, Larkin J, Ascierto PA, CheckMate C. Adjuvant Nivolumab versus Ipilimumab in Resected Stage III or IV Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(19):1824–1835. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goldberg SB, Gettinger SN, Mahajan A, Chiang AC, Herbst RS, Sznol M, Tsiouris AJ, Cohen J, Vortmeyer A, Jilaveanu L, Yu J, Hegde U, Speaker S, Madura M, Ralabate A, Rivera A, Rowen E, Gerrish H, Yao X, Chiang V, Kluger HM. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(7):976–983. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30053-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Parakh S, Park JJ, Mendis S, Rai R, Xu W, Lo S, Drummond M, Rowe C, Wong A, McArthur G, Haydon A, Andrews MC, Cebon J, Guminski A, Kefford RF, Long GV, Menzies AM, Klein O, Carlino MS. Efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with melanoma brain metastases. Br J Cancer. 2017;116(12):1558–1563. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schadendorf Dirk, Ascierto Paolo Antonio, Haanen John B. A. G., Espinosa Enrique, Demidov Lev V., Garbe Claus, Lorigan Paul, Gogas Helen, Hoeller Christoph, Guren Tormod Kyrre, Rorive Andree, Rutkowski Piotr, Muñoz-Couselo Eva, Dummer Reinhard, Carneiro Ana, Hospers Geke, Grigoryeva Elena Borisovna, Bhore Rafia, Nathan Paul. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab (NIVO) in patients with advanced melanoma (MEL) and poor prognostic factors who progressed on or after ipilimumab (IPI): Results from a phase II study (CheckMate 172) Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2017;35(15_suppl):9524–9524. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.9524. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

