Site-directed spin label electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy as a probe of conformational dynamics in the Fe(III) "locked-off" state of the CO-sensing transcription factor CooA
- PMID: 30168206
- PMCID: PMC6194275
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3449
Site-directed spin label electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy as a probe of conformational dynamics in the Fe(III) "locked-off" state of the CO-sensing transcription factor CooA
Abstract
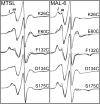
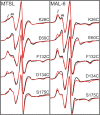
The transcriptional activator CooA belongs to the CRP/FNR (cAMP receptor protein/fumarate and nitrate reductase) superfamily of transcriptional regulators and uses heme to sense carbon monoxide (CO). Effector-driven allosteric activation is well understood in CRP, a CooA homologue. A structural allosteric activation model for CooA exists which parallels that of CRP; however, the role of protein dynamics, which is crucial in CRP, is not well understood in CooA. We employed site-directed spin labeling electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to probe CooA motions on the μs-ms timescale. We created a series of Cys substitution variants, each with a cysteine residue introduced into a key functional region of the protein: K26C, E60C, F132C, D134C, and S175C. The heme environment and DNA binding affinity of each variant were comparable to those of wild-type CooA, with the exception of F132C, which displayed reduced DNA binding affinity. This observation confirms a previously hypothesized role for Phe132 in transmitting the allosteric CO binding signal. Osmolyte perturbation studies of Fe(III) "locked-off" CooA variants labeled with either MTSL or MAL-6 nitroxide spin labels revealed that multicomponent EPR spectra report on conformational flexibility on the μs-ms timescale. Multiple dynamic populations exist at every site examined in the structurally uncharacterized Fe(III) "locked-off" CooA. This observation suggests that, in direct contrast to effector-free CRP, Fe(III) "locked-off" CooA undergoes conformational exchange on the μs-ms timescale. Importantly, we establish MAL-6 as a spin label with a redox-stable linkage that may be utilized to compare conformational dynamics between functional states of CooA.
Keywords: allostery; carbon monoxide; electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy; heme; nitroxide spin label; protein dynamics; transcription factor.
© 2018 The Protein Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Probing conformational dynamics of DNA binding by CO-sensing transcription factor, CooA.J Inorg Biochem. 2024 Oct;259:112656. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2024.112656. Epub 2024 Jul 3. J Inorg Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38986290
-
Investigation of the role of the N-terminal proline, the distal heme ligand in the CO sensor CooA.Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 9;43(44):14149-60. doi: 10.1021/bi0487948. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15518565
-
Electronic absorption, EPR, and resonance raman spectroscopy of CooA, a CO-sensing transcription activator from R. rubrum, reveals a five-coordinate NO-heme.Biochemistry. 2000 Jan 18;39(2):388-96. doi: 10.1021/bi991378g. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10631000
-
CO sensing and regulation of gene expression by the transcriptional activator CooA.J Inorg Biochem. 2000 Nov;82(1-4):51-6. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)00139-2. J Inorg Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11132638 Review.
-
Biochemical and biophysical properties of the CO-sensing transcriptional activator CooA.Acc Chem Res. 2003 Nov;36(11):825-31. doi: 10.1021/ar020097p. Acc Chem Res. 2003. PMID: 14622029 Review.
Cited by
-
How to assess the structural dynamics of transcription factors by integrating sparse NMR and EPR constraints with molecular dynamics simulations.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Apr 21;19:2097-2105. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.020. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33995905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy as a Probe of Hydrogen Bonding in Heme-Thiolate Proteins.Inorg Chem. 2019 Dec 2;58(23):16011-16027. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b02506. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31786931 Free PMC article.
-
PgRsp Is a Novel Redox-Sensing Transcription Regulator Essential for Porphyromonas gingivalis Virulence.Microorganisms. 2019 Nov 28;7(12):623. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120623. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31795139 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Monoxide-Sensing Transcription Factors: Regulators of Microbial Carbon Monoxide Oxidation Pathway Gene Expression.J Bacteriol. 2023 May 25;205(5):e0033222. doi: 10.1128/jb.00332-22. Epub 2023 May 8. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37154694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early processes in heme-based CO-sensing proteins.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Nov 3;9:1046412. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1046412. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36406263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Körner H, Sofia HJ, Zumft WG (2003) Phylogeny of the bacterial superfamily of Crp‐Fnr transcription regulators: exploiting the metabolic spectrum by controlling alternative gene programs. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:559–592. - PubMed
-
- Aono S, Nakajima H, Saito K, Okada M (1996) A novel heme protein that acts as a carbon monoxide‐dependent transcriptional activator in Rhodospirillum rubrum . Biochem Biophys Res Commun 228:752–756. - PubMed
-
- Aono S, Ohkubo K, Matsuo T, Nakajima H (1998) Redox‐controlled ligand exchange of the heme in the CO‐sensing transcriptional activator CooA. J Biol Chem 273:25757–25764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

