Serum magnesium levels and its correlation with level of control in patients with asthma: A hospital-based, cross-sectional, prospective study
- PMID: 30168460
- PMCID: PMC6120318
- DOI: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_55_18
Serum magnesium levels and its correlation with level of control in patients with asthma: A hospital-based, cross-sectional, prospective study
Abstract
Context: Magnesium (Mg) is an intracellular cation which takes part in various functions including smooth muscle contractility. Studies have shown that serum Mg level has no significant effect on asthma severity. There are only sparse data on the effect of serum Mg level on asthma control.
Aims: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of serum Mg level on asthma control.
Settings and design: This hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted at the Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal.
Subjects and methods: Our participants were adult asthma patients over 18 years of age. Asthma control was assessed using a questionnaire. Serum Mg level was estimated. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee, and informed consent was obtained from the participants.
Statistical analysis used: Welch's ANOVA test was used to analyze the correlation between serum Mg level and level of control of asthma.
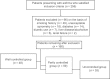
Results: We screened 256 patients who met the inclusion criteria. After 96 patients were removed based on exclusion criteria, 160 patients were grouped into three based on the level of symptom control. Forty-eight patients belonged to the "well controlled" group, 59 in "partly controlled" group, and the remaining 53 in "uncontrolled" group. The mean serum Mg level (mg/dl) was 2.08 ± 0.37, 2.07 ± 0.28, and 1.83 ± 0.34 in well, partly, and uncontrolled groups, respectively. As the level of control of asthma decreased from well controlled to uncontrolled, the level of mean serum Mg also decreased.
Conclusions: Serum Mg levels have a positive correlation with the level of symptom control in asthma. In uncontrolled asthma, serum Mg is significantly low. Hence, it might be useful as a biomarker in assessing control or severity of asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; bronchodilator agents; magnesium.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Similar articles
-
Serum Total Magnesium Level and its Correlation with Symptom Control in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma.Indian J Pediatr. 2018 Jun;85(6):420-425. doi: 10.1007/s12098-017-2599-3. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Indian J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29349628
-
Assessment of asthma control: the SERENA study.Respir Med. 2013 Nov;107(11):1659-66. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2013.08.019. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Respir Med. 2013. PMID: 24045118
-
Serum Magnesium and Vitamin D Levels as Indicators of Asthma Severity.Pulm Med. 2016;2016:1643717. doi: 10.1155/2016/1643717. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Pulm Med. 2016. PMID: 27818797 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) Level and Asthma Control Test (ATC) in Detecting GINA-Defined Asthma Control in Treated Asthmatic Patients in Vietnam.Can Respir J. 2020 Apr 25;2020:5735128. doi: 10.1155/2020/5735128. eCollection 2020. Can Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32377282 Free PMC article.
-
Weekly self-monitoring and treatment adjustment benefit patients with partly controlled and uncontrolled asthma: an analysis of the SMASHING study.Respir Res. 2010 Jun 10;11(1):74. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-74. Respir Res. 2010. PMID: 20537124 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Magnesium: The Forgotten Electrolyte-A Review on Hypomagnesemia.Med Sci (Basel). 2019 Apr 4;7(4):56. doi: 10.3390/medsci7040056. Med Sci (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30987399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Prolonged Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO 4 ) Infusion for Asthma Exacerbation in Children.J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2022 Feb 21;13(4):344-351. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1742674. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2022. PMID: 39629342 Free PMC article.
-
Serum magnesium levels and its correlation with level of control in patients with asthma: A hospital-based, cross-sectional, prospective study.Lung India. 2019 Jan-Feb;36(1):89-90. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_418_18. Lung India. 2019. PMID: 30604720 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Low Serum Levels of Zinc, Selenium, and Vitamin D3 Are Biomarkers of Airway Inflammation and Poor Asthma Control: A Two-Centre Study.Cureus. 2023 Jun 28;15(6):e41082. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41082. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37519504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodrigo G, Rodrigo C, Burschtin O. Efficacy of magnesium sulfate in acute adult asthma: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Emerg Med. 2000;18:216–21. - PubMed
-
- Ciarallo L, Brousseau D, Reinert S. Higher-dose intravenous magnesium therapy for children with moderate to severe acute asthma. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2000;154:979–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous