Antidepressants for treating depression in dementia
- PMID: 30168578
- PMCID: PMC6513376
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003944.pub2
Antidepressants for treating depression in dementia
Abstract
Background: The use of antidepressants in dementia accompanied by depressive symptoms is widespread, but their clinical efficacy is uncertain. This review updates an earlier version, first published in 2002.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy and safety of any type of antidepressant for patients who have been diagnosed as having dementia of any type and depression as defined by recognised criteria.
Search methods: We searched ALOIS, the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group's Specialised Register, on 16 August 2017. ALOIS contains information on trials retrieved from databases and from a number of trial registers and grey literature sources.
Selection criteria: We included all relevant double-blind, randomised trials comparing any antidepressant drug with placebo, for patients diagnosed as having dementia and depression.
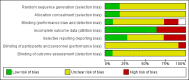
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors selected studies for inclusion and extracted data independently. We assessed risk of bias in the included studies using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool. Where clinically appropriate, we pooled data for treatment periods up to three months and from three to nine months. We used GRADE methods to assess the overall quality of the evidence.
Main results: We included ten studies with a total of 1592 patients. Eight included studies reported sufficiently detailed results to enter into analyses related to antidepressant efficacy. We split one study which included two different antidepressants and therefore had nine groups of patients treated with antidepressants compared with nine groups receiving placebo treatment. Information needed to make 'Risk of bias' judgements was often missing.We found high-quality evidence of little or no difference in scores on depression symptom rating scales between the antidepressant and placebo treated groups after 6 to 13 weeks (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.10, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.26 to 0.06; 614 participants; 8 studies). There was probably also little or no difference between groups after six to nine months (mean difference (MD) 0.59 point, 95% CI -1.12 to 2.3, 357 participants; 2 studies; moderate-quality evidence). The evidence on response rates at 12 weeks was of low quality, and imprecision in the result meant we were uncertain of any effect of antidepressants (antidepressant: 49.1%, placebo: 37.7%; odds ratio (OR) 1.71, 95% CI 0.80 to 3.67; 116 participants; 3 studies). However, the remission rate was probably higher in the antidepressant group than the placebo group (antidepressant: 40%, placebo: 21.7%; OR 2.57, 95% CI 1.44 to 4.59; 240 participants; 4 studies; moderate-quality evidence). The largest of these studies continued for another 12 weeks, but because of imprecision of the result we could not be sure of any effect of antidepressants on remission rates after 24 weeks. There was evidence of no effect of antidepressants on performance of activities of daily living at weeks 6 to 13 (SMD -0.05, 95% CI -0.36 to 0.25; 173 participants; 4 studies; high-quality evidence) and probably also little or no effect on cognition (MD 0.33 point on the Mini-Mental State Examination, 95% CI -1.31 to 1.96; 194 participants; 6 studies; moderate-quality evidence).Participants on antidepressants were probably more likely to drop out of treatment than those on placebo over 6 to 13 weeks (OR 1.51, 95% CI 1.07 to 2.14; 836 participants; 9 studies). The meta-analysis of the number of participants suffering at least one adverse event showed a significant difference in favour of placebo (antidepressant: 49.2%, placebo: 38.4%; OR 1.55, 95% CI 1.21 to 1.98, 1073 participants; 3 studies), as did the analyses for participants suffering one event of dry mouth (antidepressant: 19.6%, placebo: 13.3%; OR 1.80, 95% CI 1.23 to 2.63, 1044 participants; 5 studies), and one event of dizziness (antidepressant: 19.2%, placebo: 12.5%; OR 2.00, 95% CI 1.34 to 2.98, 1044 participants; 5 studies). Heterogeneity in the way adverse events were reported in studies presented a major difficulty for meta-analysis, but there was some evidence that antidepressant treatment causes more adverse effects than placebo treatment does.
Authors' conclusions: The available evidence is of variable quality and does not provide strong support for the efficacy of antidepressants for treating depression in dementia, especially beyond 12 weeks. On the only measure of efficacy for which we had high-quality evidence (depression rating scale scores), antidepressants showed little or no effect. The evidence on remission rates favoured antidepressants but was of moderate quality, so future research may find a different result. There was insufficient evidence to draw conclusions about individual antidepressant drugs or about subtypes of dementia or depression. There is some evidence that antidepressant treatment may cause adverse events.
Conflict of interest statement
Robert Dudas: none known Reem Malouf: none known Jenny McCleery: none known Tom Dening: none known
Figures







Update of
-
Antidepressants for treating depression in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002 Oct 21;(4):CD003944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003944. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 31;8:CD003944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003944.pub2. PMID: 12519625 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
An 2017 {published data only}
-
- An H, Choi B, Park K‐W, Kim D‐H, Yang D‐W, Hong CH, et al. The effect of escitalopram on mood and cognition in depressive Alzheimer's disease subjects. Journal of Alzheimer's disease 2017;2:727‐35. - PubMed
Banerjee 2011 {published data only}
-
- Banerjee S, Hellier J, Dewey M, Romeo R, Ballard C, Baldwin R, et al. Study of the use of antidepressants for depression in dementia: the HTA‐SADD Trial ‐ a multicentre randomised double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of the clinical effectiveness of sertraline and mirtazapine. Lancet 2011;378:403‐11. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee S, Hellier J, Romeo R, Dewey M, Knapp M, Ballard C, et al. Study of the use of antidepressants for depression in dementia: the HTA‐SADD trial ‐ a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of the clinical effectiveness and cost‐effectiveness of sertraline and mirtazapine. Health Technology Assessment March 2013; Vol. 17, issue 7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Romeo R, Knapp M, Hellier J, Dewey M, Ballard C, Baldwin R, et al. Cost‐effectiveness analyses for mirtazapine and sertraline in dementia: randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Psychiatry 2013;202:121‐8. - PubMed
de Vasconcelos 2007 {published data only}
-
- Vasconcelos Cunha UG, Lopes Rocha F, Avila de Melo R, et al. A placebo‐controlled double‐blind randomized study of venlafaxine in the treatment of depression in dementia. Dementia & Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24(1):36‐41. - PubMed
Fuchs 1993 {published data only}
-
- Fuchs A, Hehnke CH, Erhart C, Schnell C, Pramshohler B, Danninger B, et al. Video rating analysis of effect of maprotiline in patients with dementia and depression. Pharmacopsychiatry 1993;26:37‐41. - PubMed
Lyketsos 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lyketsos CG, DelCampo L, Steinberg M, Miles Q, Steele CD, Munro C, et al. Treating depression in alzheimer disease: efficacy and safety of sertraline therapy, and the benefits of depression reduction: the DIADS. Archives of General Psychiatry 2003;60(7):737‐46. - PubMed
-
- Lyketsos CG, Sheppard JME, Steele CD, Kopunke C, Baker AS, Brandt J, et al. A randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, clinical trial of sertraline in the treatment of major depression complicating Alzheimer's disease: initial results from the depression in Alzheimer's disease study. Conference Proceedings World Alzheimer Congress; 9‐13 July, 2000; Washington DC. 2000. - PubMed
-
- Mayer LS, Bay RC, Politis A, et al. Comparison of three rating scales as outcome measures for treatment trials of depression in Alzheimer disease: findings from DIADS. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006;21(10):930‐6. - PubMed
-
- Munro C, Lyketsos C. Cognitive response to sertraline treatment for depression in Alzheimer's disease: a possible sex effect. Research and Practice in Alzheimer's Disease 2006;11:361‐5.
-
- Munro CA, Brandt J, Sheppard J‐ME, Steele CD, Samus QM, Steinberg M, et al. Cognitive response to pharmacological treatment for depression in Alzheimer disease: Secondary outcomes from the depression in Alzheimer's disease study (DIADS). American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004; Vol. 12, issue 5:491‐8. - PubMed
Petracca 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Petracca G, Teson A, Chemerinski E, Leguarda R, Starkstein SE. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled study of clomipramine in depressed patients with Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 1996;8(3):270‐5. - PubMed
Petracca 2001 {published data only}
-
- Petracca GM, Chemerinski E, Starkstein SE. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of fluoxetine in depressed patients with Alzheimer's disease. International Psychogeriatrics 2001;13(2):233‐240. - PubMed
Reifler 1989 {published data only}
-
- Reifler BV, Teri L, Raskind M, Veith R, Barnes R, White E, et al. Double‐blind trial of imipramine in Alzheimer's disease patients with and without depression. American Journal of Psychiatry 1989;146(1):45‐9. - PubMed
-
- Teri L, Reifler BV, Veith RC, Barnes R, White E, McLean P, et al. Imipramine in the treatment of depressed Alzheimer's disease: impact on cognition. Journals of Gerontology: Psychological Sciences 1991;46(6):372‐7. - PubMed
Rosenberg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Flynn Longmire CV, Drye LT, Frangakis CE, Martin BK, Meinert CL, Mintzer JE, et al. Is sertraline treatment or depression remission in depressed alzheimer patients associated with improved caregiver well being? Depression In Alzheimer's Disease Study 2. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2014; Vol. 22, issue 1:14‐24. - PMC - PubMed
Roth 1996 {published data only}
-
- Roth M, Mountjoy CQ, Amrein R and the International Collaborative Study Group. Moclobemide in elderly patients with cognitive decline and depression: an international double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;168(2):149‐57. - PubMed
Weintraub 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lyketsos CG. Depression in Alzheimer's disease (DIADS 2). ClinicalTrials.gov 2004. [Study ID Numbers: 1U0166136; ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00086138]
-
- Martin BK, Frangakis CE, Rosenberg PB, et al. Design of Depression in Alzheimer's Disease Study‐2. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006;14(11):920‐30. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Barak 1996 {published data only}
-
- Barak Y, Levine J, Glasman A, Elizur A, Belmaker RH. Inositol treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a double blind, cross‐over placebo controlled trial. Progress in Neuro Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 1996;20(4):729‐36. - PubMed
Brodaty 2003 {published data only}
-
- Brodaty H, Draper BM, Millar J, Low LF, Lie D, Sharah S, et al. Randomized controlled trial of different models of care for nursing home residents with dementia complicated by depression or psychosis. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2003;64(1):63‐72. - PubMed
Bui 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bui Q. Antidepressants for agitation and psychosis in patients with dementia. American Family Physician 2012;85(1):20‐2. - PubMed
Burke 1994 {published data only}
-
- Burke WJ, Folks DG, Roccaforte WH, Wengel SP. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the treatment of coexisting depression and psychosis in dementia of the Alzheimer type. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1994;2(4):352‐4. - PubMed
Capote 1978 {published data only}
-
- Capote B, Parikh N. Cyclandelate in the treatment of senility: a controlled study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1978;26(8):360‐2. - PubMed
Choe 2014 {published data only}
-
- Choe YM, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Ryu S‐H, Choo IH, Seo EH, et al. Multi‐center, randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind clinical trial of escitalopram on the progression delaying effect in Alzheimer's disease: An MRI study for atrophy delaying effect. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2014; Vol. 10, issue 4:111.
Devanand 2003 {published data only}
-
- Devanand DP, Pelton GH, Marston K, et al. Sertraline treatment of elderly patients with depression and cognitive impairment. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18(2):123‐30. - PubMed
Drye 2012 {published data only}
Dunbar 2011 {published data only}
-
- DunbarGC, Kuchibhatla RV, Lee G. A randomized double‐blind study comparing 25 and 50 Mg Tc‐1734 (Azd3480) with placebo, in older subjects with age‐associated memory impairment. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2011;25(8):1020‐9. - PubMed
Fairweather 1993 {published data only}
-
- Fairweather DB, Kerr JS, Harrison DA, Moon CA, et al. A double blind comparison of the effects of fluoxetine and amitriptyline on cognitive function in elderly depressed patients. Human Psychopharmacology Clinical and Experimental 1993;8(1):41‐7.
Finkel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Finkel SI, Mintzer JE, Dysken M, Krishnan KR, Burt T, McRae T. A randomized, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of sertraline in the treatment of the behavioral manifestations of Alzheimer's disease in outpatients treated with donepezil. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19(1):9‐18. - PubMed
Flicker 1998 {published data only}
-
- Flicker C, Gottfries CG. Citalopram treatment of depression in elderly patients with or without dementia: results of a placebo‐controlled study. Conference Proceedings 11th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 8th‐11th March, 1998; San Diego, California, USA. 1998.
Gottfries 1991 {published data only}
-
- Gottfries CG, Nyth AL. Effect of citalopram, a selective 5‐HT reuptake blocker, in emotionally disturbed patients with dementia. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1991;640:276‐9. - PubMed
Gottfries 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gottfries CG, Karlsson I, Nyth AL. Treatment of depression in elderly patients with and without dementia disorders. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1992;6(Suppl 5):55‐64. - PubMed
Hoyberg 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hoyberg OJ, Maragakis B, Mullin J, Norum D, Stordall E, Ekdahl P, et al. A double‐blind multicentre comparison of mirtazapine and amitriptyline in elderly depressed patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1996;93(3):184‐90. - PubMed
Jenike 1985 {published data only}
-
- Jenike MA. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors as treatment for depressed patients with primary degenerative dementia (Alzheimer's disease). American Journal of Psychiatry 1985;142:763‐4. - PubMed
Karlsson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Karlsson I, Godderis J, Augusto De Mendoca Lima C, Nygaard H, Simanyi M, et al. A randomised, double‐blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of citalopram compared to mianserin in elderly, depressed patients with mild to moderate dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;15:295‐305. - PubMed
Katona 1998 {published data only}
-
- Katona CLE, Hunter BN, Bray J. A double‐blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of paroxetine and imipramine in the treatment of depression and dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1998;13:103‐8. - PubMed
Lebert 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lebert F, Stekke W, Hasenbroekx C, et al. Trazodone in fronto‐temporal dementia. Research and Practice in Alzheimer's Disease 2006;11:356‐60.
Magai 2000 {published data only}
-
- Magai C, Kennedy G, Cohen CI, Gomberg D. A controlled clinical trial of sertraline in the treatment of depression in nursing home patients with late‐stage Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;8:66‐74. - PubMed
Mizukami 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mizukami K, Hatanaka K, Tanaka Y, Sato S, Asada T. Therapeutic effects of the selective serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor milnacipran on depressive symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Progress in Neuro‐Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 2009;33(2):349‐52. - PubMed
Mokhber 2014 {published data only}
-
- Mokhber N, Abdollahian E, Soltanifar A, Samadi R, Saghebi A, Haghighi M B, et al. Comparison of sertraline, venlafaxine and desipramine effects on depression, cognition and the daily living activities in alzheimer patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 2014; Vol. 47, issue 4‐5:131‐40. - PubMed
Moretti 2003 {published data only}
-
- Moretti R, Torre P, Antonello RM, Cazzato G, Bava A. Frontotemporal dementia: paroxetine as a possible treatment of behavior symptoms. A randomized, controlled, open 14‐month study. European Neurology 2003;49(1):13‐9. - PubMed
Mossello 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mossello E, Boncinelli M, Caleri V, Cavallini MC, Palermo E, Bari M, et al. Is antidepressant treatment associated with reduced cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease?. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008;25(4):372‐9. - PubMed
Mowla 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mowla A, Mosavinasab M, Haghshenas H, Haghighi AB. Does serotonin augmentation have any effect on cognition and activities of daily living in Alzheimer's dementia? A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2007;27(5):484‐7. - PubMed
Nebes 2003 {published data only}
-
- Nebes RD, Pollock BG, Houck PR, Butters MA, Mulsant BH, Zmuda MD, et al. Persistence of cognitive impairment in geriatric patients following antidepressant treatment: a randomized, double‐blind clinical trial with nortriptyline and paroxetine. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2003;37(2):99‐108. - PubMed
Nelson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nelson JC, Hollander SB, Betzel J, et al. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets in depressed nursing home residents 85 years of age and older. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2006;21(9):898‐901. - PubMed
Nyth 1990 {published data only}
-
- Nyth AL, Gottfries CG. The clinical efficacy of citalopram in the treatment of emotional disorders in dementia disorders. British Journal of Psychiatry 1990;157:894‐901. - PubMed
Nyth 1992 {published data only}
-
- Nyth AL, Gottfries CG, Lyby K, Smedegaard‐Andersen L, Gylding‐Sabroe J, Kristensen M, et al. A controlled multicenter clinical study of citalopram and placebo in elderly patients with and without concomitant dementia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1992;86:138‐45. - PubMed
Oslin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Oslin DW, Streim JE, Katz IR, Smith BD, DiFilippo SD, Have TR, et al. Heuristic comparison of sertraline with nortriptyline for the treatment of depression in frail elderly patients. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;8(2):141‐9. - PubMed
Oslin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Oslin DW, Have TR, Streim JE, Datto CJ, Weintraub D, DiFilippo S, et al. Probing the safety of medications in the frail elderly: evidence from a randomized clinical trial of sertraline and venlafaxine in depressed nursing home residents. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2003;64(8):875‐82. - PubMed
Passeri 1987 {published data only}
-
- Passeri M, Cucinotta D, Mello M, Biziere K. Comparison of minaprine and placebo in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and multi‐infarct dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1987;2(2):97‐103.
Pelton 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pelton GH, Harper OL, Tabert MH, Sackeim HA, Scarmeas N, Roose SP, et al. Randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled donepezil augmentation in antidepressant‐treated elderly patients with depression and cognitive impairment: a pilot study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2008;23(7):670‐6. - PMC - PubMed
Pelton 2014 {published data only}
-
- Pelton GH, Soleimani L, Roose SP, Tabert MH, Cunqueiro K, Devanand DP. Olfactory identification deficits predict cognitive improvement on donepezil in antidepressant‐treated elderly patients with depression and cognitive impairment: A pilot study. Biological psychiatry 2014 Conference: 69th Annual Scientific Convention and Meeting of the Society of Biological Psychiatry. New York, NY United States: SOBP, Conference Start: 20140508 Conference End: 20140510:(var.pagings) 387S.
Peters 2011 {published data only}
-
- Peters ME, Vaidya V, Drye LT, Rosenberg P, Martin BK, Porsteinsson AP, et al. Sertraline for the treatment of depression in Alzheimer's disease: Genetic influences [conference abstract]. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry [abstracts from the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry, AAGP Annual Meeting 2011 San Antonio, TX United States. March 18‐21, 2011]. 2011; Vol. http://www.mrw.interscience.wiley.com/cochrane/clcentral/articles/795/CN....
Pollock 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pollock BG, Mulsant H, Rosen J, Mazumdar S, Blakesley RE, Houck PR, et al. A double‐blind comparison of citalopram and risperidone for the treatment of behavioral and psychotic symptoms associated with dementia. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;15(11):942‐52. - PubMed
Reynolds III 1987 {published data only}
-
- Reynolds III CF, Perel JM, Kupfer DJ, Zimmer B, Stack JA, Hoch CC. Open‐trial response of antidepressant treatment in elderly patients with mixed depression and cognitive impairment. Psychiatry Research 1997;21:111‐22. - PubMed
Rozzini 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rozzini L, Chilovi BV, Conti M, Bertoletti E, Zanetti M, Trabucchi M, et al. Efficacy of SSRIs on cognition of Alzheimer's disease patients treated with cholinesterase inhibitors. International Psychogeriatrics 2010;22(1):114‐9. - PubMed
Smith 1984 {published data only}
-
- Smith DF, Stromgren E, Petersen HN, Williams DG, Sheldon W. Lack of effect of tryptophan treatment in demented gerontopsychiatric patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1984;70:470‐7. - PubMed
Streim 2000 {published data only}
-
- Streim JE, Oslin DW, Katz IR, Smith BD, DiFilippo S, Cooper TB, et al. Drug treatment of depression in frail elderly nursing home residents. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;8(2):150‐9. - PubMed
Swartz 1997 {published data only}
-
- Swartz JR, Miller BL, Lesser IM, Darby AL. Frontotemporal dementia: treatment response to serotonin selective reuptake inhibitors. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58:212‐6. - PubMed
Taragano 1997 {published data only}
-
- Taragano FE, Lyketsos CG, Magone CA, Allegri RF, Comesana‐Diaz E. A double‐blind, randomized, fixed‐dose trial of fluoxetine vs. amitriptyline in the treatment of major depression complicating Alzheimer's disease. Psychosomatics 1997;38(3):246‐52. - PubMed
Teranishi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Teranishi M, Kurita M, Nishino S, Takeyoshi K, Numata Y, Sato T, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of risperidone, yokukansan, and fluvoxamine for the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a blinded, randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013; Vol. 33, issue 5:600‐7. - PubMed
van Asch 2013 {published data only}
-
- Asch IF, Nuyen J, Veerbeek MA, Frijters DH, Achterberg WP, Pot AM. The diagnosis of depression and use of antidepressants in nursing home residents with and without dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2013; Vol. 28, issue 3:312‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Sverdlik 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sverdlik A. Exploratory study to assess the efficacy of escitalopram versus placebo in the treatment of depressive syndrome in Alzheimers disease, vascular dementia and mixed vascular and Alzheimers dementia. ClinicalTrials.gov 2005.
Additional references
Abas 1990
-
- Abas MA, Sahakian BJ, Levy R. Neuropsychological deficits and CT scan changes in elderly depressives. Psychological Medicine 1990;20:507‐20. - PubMed
Alexopoulos 1988
-
- Alexopoulos GS, Abrams RC, Young RC, Shamoian CA. Cornell Scale for Depression in Dementia. Biological Psychiatry 1988;23(3):271‐84. - PubMed
Altman 1999
Anderson 2000
-
- Anderson IM. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors versus tricyclic antidepressants: a meta‐analysis of efficacy and tolerability. Journal of Affective Disorders 2000;58:19‐36. - PubMed
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington: APA, 1987.
Barnes 2012
Bennet 2014
-
- Bennett S, Thomas A. Depression and dementia: cause, consequence orcoincidence?. Maturitas 2014;79(2):184‐90. - PubMed
Black 2012
Burns 2002
-
- Burns A, Lawlor B, Craig S. Rating Scales in Old Age Psychiatry. British Journal of Psychiatry 2002;180:161‐7. - PubMed
Byers 2011
Diniz 2013
Farina 2017
-
- Farina N, Morrell L, Banerjee S. What is the therapeutic value of antidepressants in dementia? A narrative review. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2017;32(1):32‐49. - PubMed
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini‐mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12(3):189‐98. - PubMed
Galasko 1997
-
- Galasko D, Bennett D, Sano M, et al. An inventory to assess activities of daily living for clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11(suppl 2):33S‐39S. - PubMed
Glassman 1981
-
- Glassman AH, Bigger JT Jr. Cardiovascular effects of therapeutic doses of tricyclic antidepressants: a review. Archives of General Psychiatry 1981;38:815‐20. - PubMed
Granger 1986
-
- Granger CV, Hamilton BB, Kayton R. Functional Independence Measure. Guide for use of the uniform data set for medical rehabilitation. Buffalo, NY: Uniform Data System for Medical Rehabilitation, 1986.
Greenwald 1991
-
- Greenwald B, Kramer‐Ginsberg E, Kremen NJ, et al. Depression complicating dementia. Presented at American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting, New Orleans May 1991.
Haight 2013
-
- Haight T, Cheng H. Antidepressant treatment for older adults with dementia and depression: re‐visit the evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCT). Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2013; Vol. Conference: 2013 Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Geriatrics Society Grapevine, TX United States. Conference Start: 20130503 Conference End: 20130505.:var.pagings.
Hamilton 1960
Heser 2013
-
- Heser K, Tebarth F, Wiese B, Eisele M, Bickel H, Köhler M, et al. Age of major depression onset, depressivesymptoms, and risk for subsequent dementia: results of the German study onAgeing, Cognition, and Dementia in Primary Care Patients (AgeCoDe). Psychological Medicine 2013;43(8):1597‐610. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011 [updated March 2011]:www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Ku 2004
-
- Ku HM, Kim JH, Kwon EJ, Kim SH, Lee HS, Ko HJ, et al. A Study on the Reliability and Validity of Seoul‐Instrumental Activities of Daily Living(S‐IADL). Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association 2004;43(2):189‐99.
Leong 2014
-
- Leong C. Antidepressants for depression in patients with dementia: A review of the literature. Consultant Pharmacist 2014; Vol. 29, issue 4:254‐63. - PubMed
Leyhe 2017
-
- Leyhe T, Reynolds CF 3rd, Melcher T, Linnemann C, Klöppel S, Blennow K, et al. A common challenge in older adults:classification, overlap, and therapy of depression and dementia. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2017;13(1):59‐71. - PubMed
Loreck 1993
-
- Loreck DJ, Folstein MF. Depression in Alzheimer Disease. In: Starkstein SE, Robinson RG editor(s). Depression in Neurologic Disease. The John Hopkins series in pyschiatry and neuroscience. Baltimore, MD, US: John Hopkins University Press, 1993:50‐62.
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA work group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984;34(7):939‐44. - PubMed
Modrego 2010
-
- Modrego PJ. Depression in Alzheimer's disease. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. [Review]. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2010; Vol. 21, issue 4:1077‐87. - PubMed
Montgomery 1979
-
- Montgomery SA, Åsberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐89. - PubMed
Naismith 2010
Nelson 2011
-
- Nelson JC, Devanand DP. A systematic review and meta‐analysis of placebo‐controlled antidepressant studies in people with depression and dementia. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2011;59(4):577‐85. - PubMed
Olin 2002
-
- Olin JT, Schneider LT, Katz IR, et al. Provisional diagnostic criteria for depression of Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2002;10:125‐8. - PubMed
Orgeta 2014
Orgeta 2017
Parker 2000
-
- Parker G. Should paradigms lost be regained?. American Journal of Psychiatry 2000;157:1195‐203. - PubMed
Pfeiffer 1975
-
- Pfeiffer E. Multidimensional functional assessment: The OARS methodology. Durham, North Carolina: Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development 1975.
Raskind 1998
-
- Raskind MA. The clinical interface of depression and dementia. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1998;59(Suppl 10):9‐12. - PubMed
Ryan 2016
-
- Ryan R, Hill S. How to GRADE the quality of the evidence. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group. Version 1.0. Vol. http://cccrg.cochrane.org/author‐resources, Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group, June 2016.
Saarinen 2010
-
- Saarinen J, Kivela SL, Raiha I. [The effects of antidepressive drugs among the patients with memory disturbances—a systematic review]. Duodecim; laaketieteellinen aikakauskirja 2010; Vol. 126, issue 21:2503‐9. - PubMed
Sepehry 2012
-
- Sepehry AA, Lee PE, Hsiung GYR, Beattie BL, Jacova C. Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease with Comorbid depression: a meta‐analysis of depression and cognitive outcomes. Drugs and Aging 2012; Vol. 29, issue 10:793‐806. - PubMed
Settle Jr 1998
-
- Settle EC Jr. Antidepressant drugs: disturbing and dangerous adverse events. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1998;59(Suppl 16):25‐30. - PubMed
Starkstein 2006
-
- Starkstein SE, Mizrahi R. Depression in Alzheimer's disease. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 2006;6(6):887‐95. - PubMed
Teng 2008
Thompson 2007
-
- Thompson S, Herrmann N, Rapoport MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of antidepressants for treatment of depression in Alzheimer's disease: a metaanalysis. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry ‐ Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie 2007;52(4):248‐55. - PubMed
Vaughan 2015
Vida 1994
-
- Vida S, DesRosiers P, Carrier L, et al. Prevalence of depression in Alzheimer's disease and validity or research diagnostic criteria. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology 1994;7:238‐44. - PubMed
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Disease (ICD‐10). Geneva: WHO, 1992.
Wilkinson 1980
-
- Wilkinson IM, Graham‐White, J. Psychogeriatric dependency rating scales (PGDRS): a method of assessment for use by nurses. British Journal of Psychiatry 1980;137:558‐65. - PubMed
Williams 2000
-
- Williams JW Jr, Mulrow CD, Chiquette E, Noel PH, Aguilar C, Cornell J. A systematic review of newer pharmacotherapies for depression in adults: evidence report summary: Clinical Guidelines, Part 2. Annals of Internal Medicine 2000;132:743‐56. - PubMed
Yesavage 1982
-
- Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1982;17(1):37‐49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

