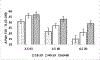Effects of manipulating the interstimulus interval on heat-evoked temporal summation of second pain across the age span
- PMID: 30169423
- PMCID: PMC6357227
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001382
Effects of manipulating the interstimulus interval on heat-evoked temporal summation of second pain across the age span
Abstract
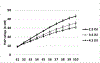
This study examined the effects of interstimulus interval (ISI) on heat-evoked temporal summation of second pain (TSSP) and tested whether greatest maintenance of TSSP would occur at longer ISIs in older adults. Several lines of evidence support that TSSP is associated with central sensitization and is centrally mediated. The participants were 198 community-dwelling adults divided into 3 age cohorts (18-39, 40-59, and 60-78 years of age). Six TSSP trials used a train of 10 contacts with a preheated probe that made repetitive contact with the volar forearm. Participants completed 2 trials at each ISI of 2.5, 3.5, and 4.5 seconds. The intraclass correlations for each pair of trials support the reliability of the current methodology. Temporal summation of second pain scores declined in a time-dependent manner across ISI. In addition, greater maintenance of TSSP at longer ISIs was observed in middle-aged and older age groups compared with the younger cohort. Significant associations were found between TSSP and measures of recent pain. Greater summation at longer ISIs in older adults would suggest slower decay of excitability in spinal neurons and infer increased risk for central sensitization with advancing age.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Temporal summation of second pain and its maintenance are useful for characterizing widespread central sensitization of fibromyalgia patients.J Pain. 2007 Nov;8(11):893-901. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2007.06.006. Epub 2007 Aug 3. J Pain. 2007. PMID: 17681887 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal summation of second pain: variability in responses to a fixed protocol.Eur J Pain. 2013 Jan;17(1):67-74. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00190.x. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Eur J Pain. 2013. PMID: 22899549 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of temporal summation of second pain sensations elicited by brief contact of glabrous skin by a preheated thermode.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Aug;78(2):992-1002. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.2.992. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9307129 Clinical Trial.
-
Association Between Borderline Personality Features and Temporal Summation of Second Pain: A Cross-Sectional Study.Behav Med. 2017 Jul-Sep;43(3):208-217. doi: 10.1080/08964289.2017.1322935. Behav Med. 2017. PMID: 28767017
-
Why look in the brain for answers to temporomandibular disorder pain?Cells Tissues Organs. 2005;180(1):69-75. doi: 10.1159/000086200. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005. PMID: 16088135 Review.
Cited by
-
The silent epidemic of chronic pain in older adults.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Jul 13;93:284-290. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31004724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between smoking and central sensitization pain: a web-based cross-sectional study.J Anesth. 2024 Apr;38(2):198-205. doi: 10.1007/s00540-023-03302-4. Epub 2024 Jan 24. J Anesth. 2024. PMID: 38265695 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of Electro-Dry Needling Does Not Change the Pain Response After Repeated Nociceptive Thermal Stimuli in Asymptomatic Individuals: A Randomized Intervention Study.Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2023 Apr 17;5(2):100267. doi: 10.1016/j.arrct.2023.100267. eCollection 2023 Jun. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2023. PMID: 37312978 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced analgesia: an evaluation of effects on temporal summation of pain and the role of endogenous opioid mechanisms.Pain Rep. 2022 Feb 8;7(2):e987. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000987. eCollection 2022 Mar-Apr. Pain Rep. 2022. PMID: 35155968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arendt-Nielsen L, Petersen-Felix S, Fischer M, Bak P, Bjerring P, Zbinden AM. The effect of Nmethyl-Daspartate antagonist (ketamine) on single and repeated nociceptive stimuli: a placebo-controlled experimental human study. Anesth Analg 1995;81: 63–68. - PubMed
-
- Blalock SJ, DeVellis RF, Brown GK, Wallston KA. Validity of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale in arthritis populations. Arthritis Rheum 1989;32:991–7. - PubMed
-
- Cathcart S, Winefield AH, Lushington K, Rolan P. Noxious inhibition of temporal summation is impaired in chronic tension-type headache. Headache 2010;50(3):403–12. - PubMed
-
- Davies SN, Lodge D. Evidence for involvement of N-methylaspartate receptors in ‘wind-up’ of class 2 neurones in the dorsal horn of the rat. Brain Res 1987;424:402–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical