A comprehensive evaluation of the genetic architecture of sudden cardiac arrest
- PMID: 30169657
- PMCID: PMC6247663
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy474
A comprehensive evaluation of the genetic architecture of sudden cardiac arrest
Abstract
Aims: Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) accounts for 10% of adult mortality in Western populations. We aim to identify potential loci associated with SCA and to identify risk factors causally associated with SCA.
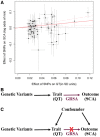
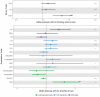
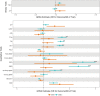
Methods and results: We carried out a large genome-wide association study (GWAS) for SCA (n = 3939 cases, 25 989 non-cases) to examine common variation genome-wide and in candidate arrhythmia genes. We also exploited Mendelian randomization (MR) methods using cross-trait multi-variant genetic risk score associations (GRSA) to assess causal relationships of 18 risk factors with SCA. No variants were associated with SCA at genome-wide significance, nor were common variants in candidate arrhythmia genes associated with SCA at nominal significance. Using cross-trait GRSA, we established genetic correlation between SCA and (i) coronary artery disease (CAD) and traditional CAD risk factors (blood pressure, lipids, and diabetes), (ii) height and BMI, and (iii) electrical instability traits (QT and atrial fibrillation), suggesting aetiologic roles for these traits in SCA risk.
Conclusions: Our findings show that a comprehensive approach to the genetic architecture of SCA can shed light on the determinants of a complex life-threatening condition with multiple influencing factors in the general population. The results of this genetic analysis, both positive and negative findings, have implications for evaluating the genetic architecture of patients with a family history of SCA, and for efforts to prevent SCA in high-risk populations and the general community.
Figures
Comment in
-
Can genetics predict risk for sudden cardiac death? The relentless search for the Holy Grail.Eur Heart J. 2018 Nov 21;39(44):3970-3972. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy508. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30188985 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Ferranti S. D, Després J-P, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Willey JZ, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB.. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014;CIR.0000000000000152. - PubMed
-
- Blom MT, Beesems SG, Homma PCM, Zijlstra JA, Hulleman M, van Hoeijen DA, Bardai A, Tijssen JGP, Tan HL, Koster RW.. Improved survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and use of automated external defibrillators. Circulation 2014;130:1868–1875. - PubMed
-
- Friedlander Y, Siscovick DS, Weinmann S, Austin MA, Psaty BM, Lemaitre RN, Arbogast P, Raghunathan TE, Cobb LA.. Family history as a risk factor for primary cardiac arrest. Circulation 1998;97:155–160. - PubMed
-
- Jouven X, Desnos M, Guerot C, Ducimetière P.. Predicting sudden death in the population: the Paris Prospective Study I. Circulation 1999;99:1978–1983. - PubMed
-
- Dekker LRC, Bezzina CR, Henriques JPS, Tanck MW, Koch KT, Alings MW, Arnold AER, Boer M-J. D, Gorgels APM, Michels HR, Verkerk A, Verheugt FWA, Zijlstra F, Wilde AAM.. Familial sudden death is an important risk factor for primary ventricular fibrillation: a case-control study in acute myocardial infarction patients. Circulation 2006;114:1140–1145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088456/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL046959/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL034594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL026490/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088576/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA040360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM104469/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007814/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL034595/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091244/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL035464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL054776/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111089/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111267/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA034944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

