Effect of Milking Method, Diet, and Temperature on Venom Production in Scorpions
- PMID: 30169760
- PMCID: PMC6121513
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/iey081
Effect of Milking Method, Diet, and Temperature on Venom Production in Scorpions
Abstract
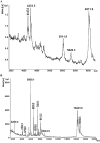
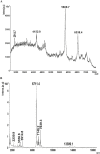
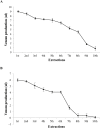
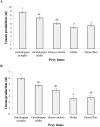
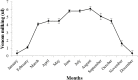
In the present study, two common buthid scorpions, i.e., Androctonus finitimus (Pocock, 1897) (Scorpiones: Buthidae) and Hottentota tamulus (Fabricus, 1798) (Scorpiones: Buthidae), were maintained in the laboratory for venom recovery. The aim of study was to compare the quantity and quality of venom extracted from scorpions by manual and electrical method. We also recorded the effect of diet and temperature on venom production. Results of our study revealed that electrical method yielded good quality and higher quantity of venom as compared to manual method. The quantity of venom by two studied species differed statistically. We recorded the effect of food on venom production by providing different prey items to the scorpions and found that grasshopper nymphs and adults were the best diet for the scorpions to get maximum yield of venom as compared to other prey types (house crickets, house flies, and moths). Production of venom and activity of scorpions was found to be associated with temperature. During winter season, venom recovery was comparatively low as compared to the hottest part of year; when venom milking and activity of scorpions both were increased.
Figures






References
-
- Ahsan M. M., and Tahir H. M.. 2016. Foraging behaviour of Hottentotta tumulus (Fabricius, 1798) and Odontobuthus odonturus (Pocock, 1897). Pakistan J. Zoo. 48: 1811–1815.
-
- Al Asmari A. K., H. A. Khan R. A. Manthiri K. M. Al Yahya, and Al Otaibi K. E.. 2014. Effects of Echis pyramidum snake venom on hepatic and renal antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 28: 407–412. - PubMed
-
- Almaaytah A. and Albalas Q.. 2014. Scorpion venom peptides with no disulfide bridges: a review. Peptides. 51: 35–45. - PubMed
-
- Andreotti N., Jouirou B., Mouhat S., Mouhat L., and Sabatier J. M.. 2010. Therapeutic value of peptides from animal venoms, pp. 287–303. In H. W. Liu, and L. Mander (eds.), Amino acids, peptides and proteins, comprehensive natural products II: chemistry and biology. Elsevier, Oxford.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

