Circadian rhythm of cardiac electrophysiology, arrhythmogenesis, and the underlying mechanisms
- PMID: 30170229
- PMCID: PMC6520649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.08.026
Circadian rhythm of cardiac electrophysiology, arrhythmogenesis, and the underlying mechanisms
Abstract
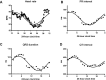
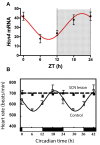
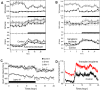
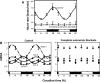
Cardiac arrhythmias are a leading cause of cardiovascular death. It has long been accepted that life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and sudden cardiac death) are more likely to occur in the morning after waking. It is perhaps less well recognized that there is a circadian rhythm in cardiac pacemaking and other electrophysiological properties of the heart. In addition, there is a circadian rhythm in other arrhythmias, for example, bradyarrhythmias and supraventricular arrhythmias. Two mechanisms may underlie this finding: (1) a central circadian clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus may directly affect the electrophysiology of the heart and arrhythmogenesis via various neurohumoral factors, particularly the autonomic nervous system; or (2) a local circadian clock in the heart itself (albeit under the control of the central clock) may drive a circadian rhythm in the expression of ion channels in the heart, which in turn varies arrhythmic substrate. This review summarizes the current understanding of the circadian rhythm in cardiac electrophysiology, arrhythmogenesis, and the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; Autonomic nervous system; Cardiac conduction system; Cardiac pacemaking; Circadian rhythm; Ion channel remodeling.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

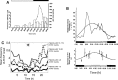
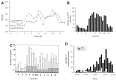
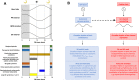
References
-
- Portaluppi F., Hermida R.C. Circadian rhythms in cardiac arrhythmias and opportunities for their chronotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:940–951. - PubMed
-
- Davidson A.J., London B., Block G.D., Menaker M. Cardiovascular tissues contain independent circadian clocks. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2005;27:307–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

